Genetics
Resources › Life Sciences Resources» Next
Related Articles
[stage_edit] =>
[body] =>
My years at ICR have been punctuated by numerous creation/evolution debates, but actually my first such debate came as a sophomore in high school. When the issue came up, I was selected to "debate" the class evolutionist.
My opponent began her presentation by defining evolution as simply "change over time." She documented many examples of change in non-living things as well as plants and animals. Even people change over time. We are, on average, taller than our ancestors just a few generations ago. As a population certainly we age. No one could dispute that these changes have occurred, thus she had "proven" that evolution had occurred.
And therein lies the crux of the matter. You simply must define terms carefully. Evolution in the meaningful sense implies big changes, like a fish turning into a person. Has this happened? Do the small changes we observe over time add up to the big changes needed by evolution? Did a single-celled organism become a marine invertebrate, then a fish, then an amphibian, then a reptile, then a mammal, then an ape-like ancestor then a person? These truly big changes must have occurred if evolution really accounts for all of life.
It's instructive to try to imagine what must happen to turn a cell into an invertebrate, or a worm into a fish, or a fish into an amphibian, etc. List the structural changes needed. A cell doesn't have the genes needed to produce even a simple nodal chord, nor does a fish have the genes to produce legs. This extra genetic information must be added from some external source, but science knows of no such source. Mutations do produce novel genetic changes, but never has a mutation been known to add coded information to an already complex DNA system. On the contrary, it usually and easily causes a deterioration of the information present in the DNA. For random mutations to add the information for a leg where there is none is asking a lot, in fact, asking too much. Never has a helpful mutation been observed, yet trillions are needed.
Listing all the differences between a fish and an amphibian, or a reptile and a bird, or reptile and mammal helps to clarify the immensity of evolution's task. Not only are there skeletal changes, but think of the totally new organs needed, different reproductive systems, altered respiratory and cardiovascular make-up, thermal schemes and on and on.
Step back and take a look at the big picture. Evolution, as a concept of everything, is worse than non-science, it is nonsense. The highly complex information laden DNA code cannot yet even be read by today's genomists. How could it have written itself by chance mutation or genetic recombination. Surely some things simply cannot be.
When a vote was taken as to who won the debate, I came out on top 32-1. The lone vote for evolution was an exchange student from Marxist China, and even he admitted I had the better arguments. He just didn't dare vote against the party line.
Maybe that's the key. It takes a prior, gut-level commitment to evolution to continue to favor it in spite of the weight of evidence to the contrary.
[body_edit] =>
My years at ICR have been punctuated by numerous creation/evolution debates, but actually my first such debate came as a sophomore in high school. When the issue came up, I was selected to "debate" the class evolutionist.
My opponent began her presentation by defining evolution as simply "change over time." She documented many examples of change in non-living things as well as plants and animals. Even people change over time. We are, on average, taller than our ancestors just a few generations ago. As a population certainly we age. No one could dispute that these changes have occurred, thus she had "proven" that evolution had occurred.
And therein lies the crux of the matter. You simply must define terms carefully. Evolution in the meaningful sense implies big changes, like a fish turning into a person. Has this happened? Do the small changes we observe over time add up to the big changes needed by evolution? Did a single-celled organism become a marine invertebrate, then a fish, then an amphibian, then a reptile, then a mammal, then an ape-like ancestor then a person? These truly big changes must have occurred if evolution really accounts for all of life.
It's instructive to try to imagine what must happen to turn a cell into an invertebrate, or a worm into a fish, or a fish into an amphibian, etc. List the structural changes needed. A cell doesn't have the genes needed to produce even a simple nodal chord, nor does a fish have the genes to produce legs. This extra genetic information must be added from some external source, but science knows of no such source. Mutations do produce novel genetic changes, but never has a mutation been known to add coded information to an already complex DNA system. On the contrary, it usually and easily causes a deterioration of the information present in the DNA. For random mutations to add the information for a leg where there is none is asking a lot, in fact, asking too much. Never has a helpful mutation been observed, yet trillions are needed.
Listing all the differences between a fish and an amphibian, or a reptile and a bird, or reptile and mammal helps to clarify the immensity of evolution's task. Not only are there skeletal changes, but think of the totally new organs needed, different reproductive systems, altered respiratory and cardiovascular make-up, thermal schemes and on and on.
Step back and take a look at the big picture. Evolution, as a concept of everything, is worse than non-science, it is nonsense. The highly complex information laden DNA code cannot yet even be read by today's genomists. How could it have written itself by chance mutation or genetic recombination. Surely some things simply cannot be.
When a vote was taken as to who won the debate, I came out on top 32-1. The lone vote for evolution was an exchange student from Marxist China, and even he admitted I had the better arguments. He just didn't dare vote against the party line.
Maybe that's the key. It takes a prior, gut-level commitment to evolution to continue to favor it in spite of the weight of evidence to the contrary.
[typeID] => 3
[visible] => t
[pdf] =>
[publishURL] => can-small-we-see-add-up-big-changes-needed-for-evo
[publishDate] => 0000-00-00
[authorAsterisk] => f
[domainID] => 1
[publication] =>
[volume] =>
[issue] =>
[page] =>
[author] => John D. Morris, Ph.D.
)
-->
When I was in Moscow a couple of years ago, I lectured to a large group of biology teachers and museum curators at the Museum of Biology in Moscow. After my talk, which was enthusiastically received by all present (except the two Ph.D.'s from the nearby Museum of Evolution), I was given a tour of the museum. Hundreds of school students visit each day, in addition to others of the public. Thus the exhibits were geared to convince students that there is no doubt about evolution—a vital point in Communist education.
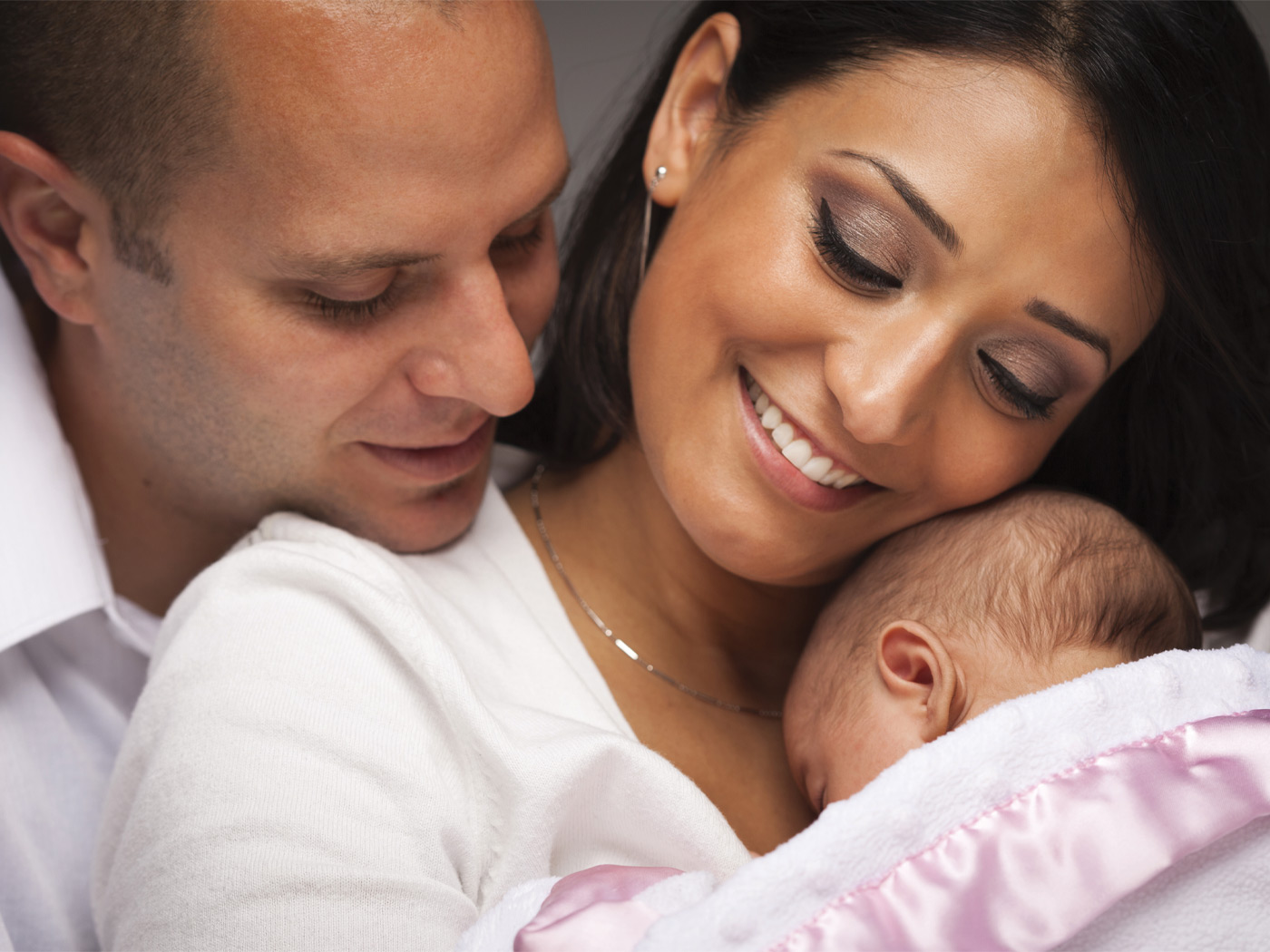
One exhibit (in the Darwin Room) was especially effective. As gruesome as it seems, newborn babies, in jars of formaldehyde, were displayed, all of whom exhibited some abnormality which seemed to be a "throwback" to animal ancestry.
One baby had several pairs of nipples in a "nipple line," showing relationship to a dog or pig. Another baby was covered with hair, and was called a "monkey baby." Still another had a "tail." There is no doubt, they believe—humans descended from animals.
This was not my first exposure to such evidences. I had been forced to seek out an answer when all three points were brought out in a debate against a biology professor in Long Beach, California.
As it turns out, evolutionists who know something about these problems don't consider them to be an argument for evolution. Instead, these abnormalities represent fetal development problems, and have nothing at all to do with ancestry. Even more serious abnormalities do occur in a host of expressions, which bear no resemblance at all to any possible ancestor.
You see, almost every cell in the developing fetus (and in the adult body) contains the complete genetic code. Thus each cell possesses, in principle, the information necessary to grow into muscle, bone, teeth, blood, nerve, or organ.
Normal development requires an amazing sequence of events. Growth of each component must occur at the proper time and to the proper extent. Throughout the growth, a variety of proteins are secreted which trigger the growth. The lack of the protein trigger, or the improper amount, or faulty timing will produce abnormal development. The marvelous DNA code oversees and governs this development in a healthy environment.
But if the environment undergoes some sort of shock, this intricate sequence could be interrupted. Examples of this shock might be due to malnutrition, or be drug induced, or temperature related, or even due to physical impact.
The most important thing to remember is that the damaged information which produced these developmental abnormalities is not usually present in the reproductive cells, and thus is not passed on to offspring. A person born with multiple nipples can grow to maturity and have children, and their children would have no greater likelihood of having multiple nipples than any other child has. Since the expressed trait is not inherited, it obviously was not inherited from one's ancestors, whether animal or not.
Why, then, is this used as evidence for evolution? Beats me! I guess there's just nothing better to use.
*Dr. John Morris is the President of ICR.
[body_edit] =>
When I was in Moscow a couple of years ago, I lectured to a large group of biology teachers and museum curators at the Museum of Biology in Moscow. After my talk, which was enthusiastically received by all present (except the two Ph.D.'s from the nearby Museum of Evolution), I was given a tour of the museum. Hundreds of school students visit each day, in addition to others of the public. Thus the exhibits were geared to convince students that there is no doubt about evolution—a vital point in Communist education.
One exhibit (in the Darwin Room) was especially effective. As gruesome as it seems, newborn babies, in jars of formaldehyde, were displayed, all of whom exhibited some abnormality which seemed to be a "throwback" to animal ancestry.
One baby had several pairs of nipples in a "nipple line," showing relationship to a dog or pig. Another baby was covered with hair, and was called a "monkey baby." Still another had a "tail." There is no doubt, they believe—humans descended from animals.
This was not my first exposure to such evidences. I had been forced to seek out an answer when all three points were brought out in a debate against a biology professor in Long Beach, California.
As it turns out, evolutionists who know something about these problems don't consider them to be an argument for evolution. Instead, these abnormalities represent fetal development problems, and have nothing at all to do with ancestry. Even more serious abnormalities do occur in a host of expressions, which bear no resemblance at all to any possible ancestor.
You see, almost every cell in the developing fetus (and in the adult body) contains the complete genetic code. Thus each cell possesses, in principle, the information necessary to grow into muscle, bone, teeth, blood, nerve, or organ.
Normal development requires an amazing sequence of events. Growth of each component must occur at the proper time and to the proper extent. Throughout the growth, a variety of proteins are secreted which trigger the growth. The lack of the protein trigger, or the improper amount, or faulty timing will produce abnormal development. The marvelous DNA code oversees and governs this development in a healthy environment.
But if the environment undergoes some sort of shock, this intricate sequence could be interrupted. Examples of this shock might be due to malnutrition, or be drug induced, or temperature related, or even due to physical impact.
The most important thing to remember is that the damaged information which produced these developmental abnormalities is not usually present in the reproductive cells, and thus is not passed on to offspring. A person born with multiple nipples can grow to maturity and have children, and their children would have no greater likelihood of having multiple nipples than any other child has. Since the expressed trait is not inherited, it obviously was not inherited from one's ancestors, whether animal or not.
Why, then, is this used as evidence for evolution? Beats me! I guess there's just nothing better to use.
*Dr. John Morris is the President of ICR.
[typeID] => 3 [visible] => t [pdf] => [publishURL] => why-do-some-babies-show-animal-characteristics [publishDate] => 0000-00-00 [authorAsterisk] => f [domainID] => 1 [publication] => [volume] => [issue] => [page] => [author] => John D. Morris, Ph.D. ) -->