The cartilage-containing fossil named Caudipteryx came from China’s famous Jehol Biota. Although the study authors along with most scientists labeled it a dinosaur, other workers consider it an extinct flightless bird.2 Regardless, why should anyone believe that it could retain chromatin—packed up DNA—after so long?
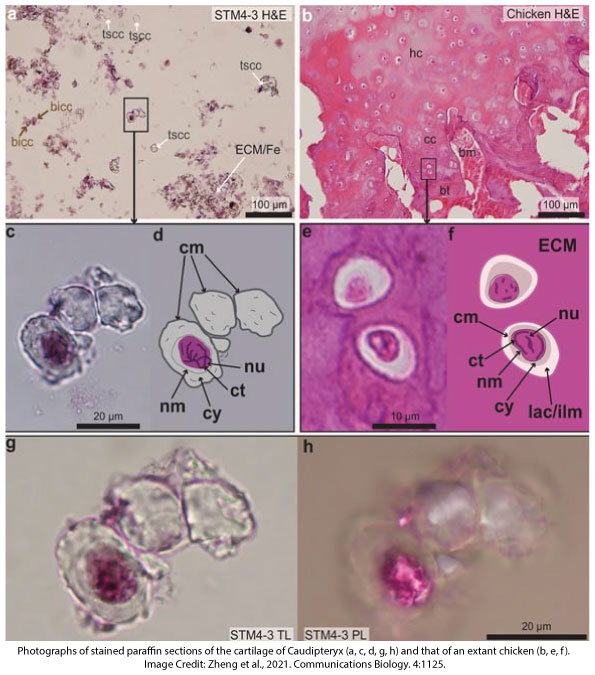
The team mounted thin sections onto microscope slides of cartilage from the extinct animal’s knee joint. They applied a standard biology stain for DNA called H&E (Hematoxylin and Eosin.) Hematoxylin colors DNA purple, and Eosin color proteins pink. The team found purple and pink right where they should be if the Caudipteryx cells were harvested recently.
The report included images of stained chromatin from the fossil alongside stained chromatin in modern chicken cartilage. The study authors wrote, “When this stained dinosaur cell is compared to stained avian chondrocytes, an identical staining pattern can be seen.”1 What pattern, exactly? “The two specimens reacted identically, and one dinosaur chondrocyte revealed a nucleus with fossilized threads of chromatin.”
But the term “fossilized” cannot here mean that minerals replaced the DNA. If so, then the stain would not have worked. Bundles of DNA inside cell nuclei can only come from remnants of real chromatin still in the fossil. So far, so good. But what science supports the part where they assert the chromatin has lasted for millions of years?
The study authors repeated the importance of rapid mineralization to the preservation of cells to help justify this claim. They said that “permineralization may have occurred within a few days to a few weeks after death, before chondrocyte autolysis could start.”1 Autolysis refers to the way that loose enzymes ordinarily digest cells within a few months of death.
Yes, some process needs to arrest autolysis—and microbes—for any hope of preserving biomolecules, but that or another process would also need to arrest regular old chemistry. The study authors offered no speculation about how oxidation or hydrolysis, for example, could have failed for so long back then while working so relentlessly today.
Why the silence? Possibly it’s best to not even mention problems for which one has no answers.
DNA decay rate studies show that it cannot last that long.3 Not even close.
So, just like the one hundred other reports of original biomaterials like DNA and proteins in fossils, this confirms young-looking biomolecules still rest inside ancient fossils. And the silent treatment about DNA decay rates align with the idea that cartilage cells with chromatin looks much younger than its evolutionary age assignment.4,5
References
1. Zheng, X., et al. 2021. Nuclear preservation in the cartilage of the Jehol dinosaur Caudipteryx. Communications Biology. 4:1125.
2. See references in: Thomas, B., and J. Sarfati. Researchers remain divided over ‘feathered dinosaurs.’ Journal of Creation. 32(1): 121-127.
3. Allentoft, M. E. et al. 2012. The half-life of DNA in bone: measuring decay kinetics in 158 dated fossils. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 279(1748): 4724-33.
4. Thomas, B. and S. Taylor. 2019. Proteomes of the past: the pursuit of proteins in paleontology. Expert Review of Proteomics. 16 (11-12): 881-895.
5. List of Biomaterial Fossil Papers. Google doc. Accessed October 7, 2021.
Dr. Brian Thomas is a Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool.















