In their quest to try and find some sort of evolutionary similarity between humans and apes, scientists have compared DNA, proteins, anatomy, behavior, and every other conceivable feature. But many of these attempts showed that a huge chasm of dissimilarity exists with no distinct evolutionary connection. And now, a new study comparing saliva between humans and apes is once again showing the uniqueness of humans and the failure of evolutionary reasoning.1
Your saliva is a highly designed and precise combination of important proteins required for preprocessing food in your mouth prior to entering your digestive tract. Human saliva also contains other specific types of proteins needed for the maintenance of tooth mineralization and protection from microbial pathogens. The sum total of the complement of proteins in saliva is called the salivary proteome.
In a recent research study, scientists compared the salivary proteomes of humans with two ape species considered to be our closest living evolutionary relatives: chimpanzees and gorillas. They also included monkeys (Rhesus macaque) as an evolutionary out-group—an alleged distant relative.
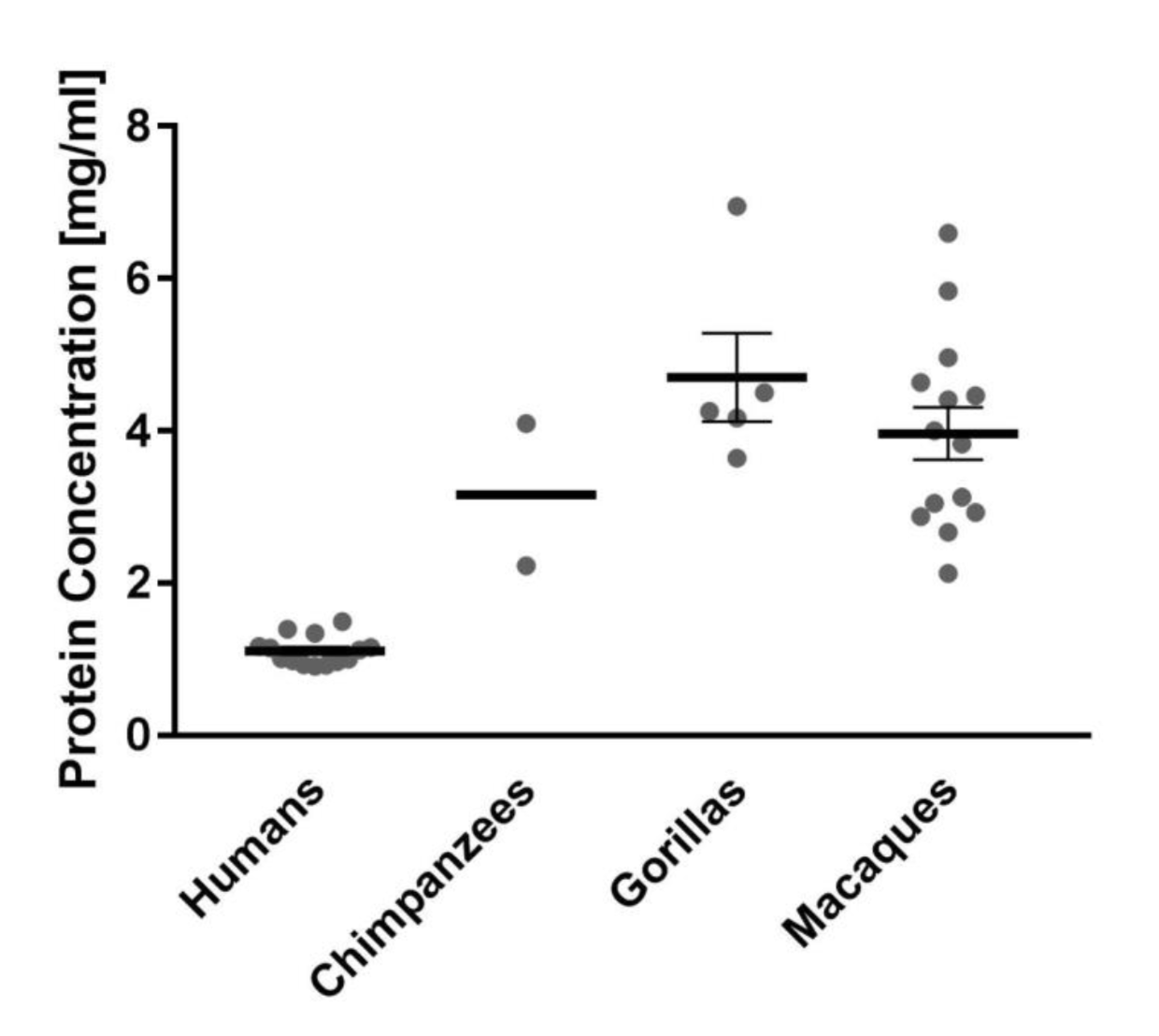
The first major difference the researchers noted was that human saliva is much more watery and diluted than apes’ and the overall concentration of proteins is much lower. In fact, human saliva contains half the total amount of proteins compared to apes and macaques (see figure).
The next thing the scientists observed was that the concentrations of the major groups of proteins is markedly different between humans and apes as well. The researchers also noted that human-specific proteins were found that do not exist in apes. Overall, the salivary proteomes were distinctly different between not just humans and apes, but also between chimps, gorillas, and macaques.
In their conclusion, the researchers stated, “We discovered unique protein profiles in saliva of humans that were distinct from those of nonhuman primates.” They also claimed, “Certain properties and components of human and nonhuman primate saliva might have evolved in a lineage-specific manner.”1 The term “lineage specific” means there is no evolutionary overlap; each human, ape, and monkey salivary proteome is unique.
This observance doesn’t line up with evolution, but fits well with Genesis that tells us God created each type of creature after its kind.2 Humans, chimps, gorillas, and macaques are unique kinds, and both science and scripture continue to confirm this biological truth.
References
1. Thamadilok, S. et al. 2020. Human and Nonhuman Primate Lineage-Specific Footprints in the Salivary Proteome. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 37 (2): 395-405.
2. Genesis 1:21, 25
Dr. Tomkins is Life Sciences Director at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his doctorate in genetics from Clemson University.
Ape Spit Radically Different from Human
The Latest
Confirmed New Record for Most Distant Galaxy
A galaxy with the designation MoM-z14 has recently been confirmed as the most distant galaxy ever detected.1,2 By Big Bang reckoning, we...
Insect Eyes Reflect Creation
Research into insect eyes continues to reveal amazing structure and function. For example, although fruit flies’ eyes are attached firmly to their...
February 2026 ICR Wallpaper
"Be strong and of good courage, do not fear nor be afraid of them; for the LORD you God, He is the One who goes with you. He will not leave you...
Microgravity's Effect on Bacteriophages Is Not Evolution
The word evolution is often used imprecisely, leading the public to believe that any biological change is evolution, and, therefore, it’s a fact.1...
Engineered for Extremes: The Hidden Precision of a Salt Lake...
Water that is nearly five times saltier than the ocean is deadly to most animals. But in Utah’s Great Salt Lake, scientists have found a tiny...
CREATION PODCAST
Giant Sequoias: Too Complex to Be Accidental | The Creation Podcast:...
What living thing grows taller than a 25-story building, survives raging wildfires, and actually depends on those fires to reproduce? Giant sequoias...
Bound by Design: How a Universal Temperature Law Reveals Life’s...
What if every living creature—from coral reefs and cold-water fish to mountain flowers and desert reptiles—followed the same hidden temperature...
The Flood Explains 18,000 Dinosaur Tracks in Bolivia
A new discovery of 18,000 individual dinosaur tracks in the Bolivian El Molino Formation contains the highest number of theropod dinosaur tracks in...
Prolonged 40-Year Growth in T. Rex: Evidence for Pre-Flood Longevity?
An open access 2026 PeerJ research paper claims that T. rex took 40 years to reach its full adult body size, in contrast to a much shorter previous...
Recent Discovery of a Strange Microbe Gives No Clues to Evolution
Research into God’s living creation is dynamic and always surprising. This is true whether one peers into the deepest reaches of space or dives...