 One of the most important aspects of any Flood model is the definition of its boundaries. Is there an identifiable layer in the rock record where we can say the global Flood ended? And should we expect that boundary to be at a consistent level globally? ICR’s Column Project research team compiled global rock data from oil wells and outcrops to help answer these questions.
One of the most important aspects of any Flood model is the definition of its boundaries. Is there an identifiable layer in the rock record where we can say the global Flood ended? And should we expect that boundary to be at a consistent level globally? ICR’s Column Project research team compiled global rock data from oil wells and outcrops to help answer these questions.
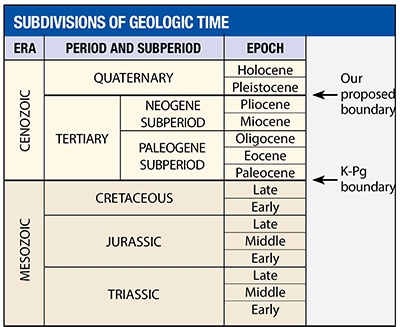
Most creation scientists agree that the Flood/post-Flood boundary is at or near one of two levels: 1) the top of the Cretaceous system at the K-Pg horizon,1,2 or 2) near the top of the Upper Cenozoic at about the Pliocene level (Figure 1).3,4
Our research results include five major geological observations that demonstrate the boundary must be at or near the Pliocene level.5 Some of these observed features are so massive and/or extraordinary that local post-Flood catastrophes could not have produced them as the K-Pg boundary proponents have claimed. Our recently published technical article describes these features in depth, but this article will summarize our most significant findings so far.5
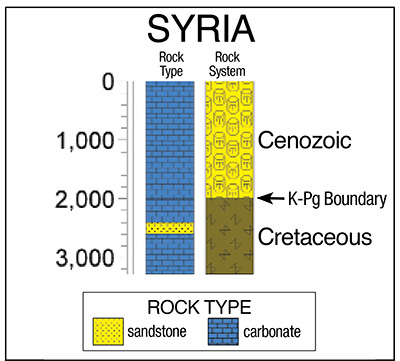
Probably the strongest evidence of the Pliocene boundary is the presence of uninterrupted carbonate rocks from the Cretaceous level below the K-Pg boundary and continuing upward through Miocene strata across much of North Africa and the Middle East, including the countries of Syria and Iraq (Figure 2). Carbonate can only form underwater, which tells us these layers were still under the Flood’s waters at the time of deposition. These water-deposited sediments across such a broad region are compelling proof that the floodwaters could not have receded fully from this area until the Late Miocene and possibly even later.
Incidentally, Syria and Iraq are just to the south of the site in Turkey where the Bible describes the Ark landing. Huge regions of the Middle East were clearly still underwater during most of the Cenozoic. This means active ocean sedimentation would have made it impossible for humans to settle there and build the Tower of Babel at that time.
Our studies of the stratigraphic column data across Europe produced the same results as our observations in the Middle East and North Africa. Uninterrupted layers of marine strata are found from the Cretaceous level upward through the Miocene across much of Central Europe, including Bulgaria, Romania, Italy, Austria, and even the Netherlands.
From all of these data, we concluded that too much water-deposited sediment was still being actively emplaced for the Flood to be over at the level of the K-Pg boundary. Much of the Cenozoic (Paleogene and Neogene) was still undergoing active marine deposition and was likely part of the receding phase of the great Flood. The post-Flood boundary must be near the top of the upper Neogene, around the Pliocene level.
As our Flood research continues and we refine our interpretations, we’re getting a clearer picture of this world-changing event. ![]()
Our research has identified a globally consistent and identifiable change from marine to non-marine deposition in the Upper Cenozoic rock layers, coinciding with an abrupt change in fossil content.6 Both forms of evidence confirm the Pliocene as the more accurate Flood boundary. As our Flood research continues and we refine our interpretations, we’re getting a clearer picture of this world-changing event.
References
- Austin, S. A. et al. 1994. Catastrophic Plate Tectonics: A Global Flood Model of Earth History. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Creationism. R. E. Walsh, ed. Pittsburgh, PA: Creation Science Fellowship, 609-621.
- Whitmore, J. H. and K. P. Wise. 2008. Rapid and early post-Flood mammalian diversification evidences in the Green River Formation. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Creationism. A. A. Snelling, ed. Pittsburgh, PA: Creation Science Fellowship, 449-457.
- Oard, M. J. 2013. Geology indicates the terrestrial Flood/post-Flood boundary is mostly in the Late Cenozoic. Journal of Creation. 27 (1): 119-127.
- Clarey, T. L. 2016. The Ice Age as a mechanism for post-Flood dispersal. Journal of Creation. 30 (2): 48-53.
- Clarey, T. L. 2017. Local Catastrophes or Receding Floodwater? Global Geologic Data that Refute a K-Pg (K-T) Flood/post-Flood Boundary. Creation Research Society Quarterly. 54 (2): 100-120.
- Pimiento, C. et al. 2017. The Pliocene marine megafauna extinction and its impact on functional diversity. Nature Ecology & Evolution. 1: 1100-1106.
* Dr. Clarey is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in geology from Western Michigan University.










