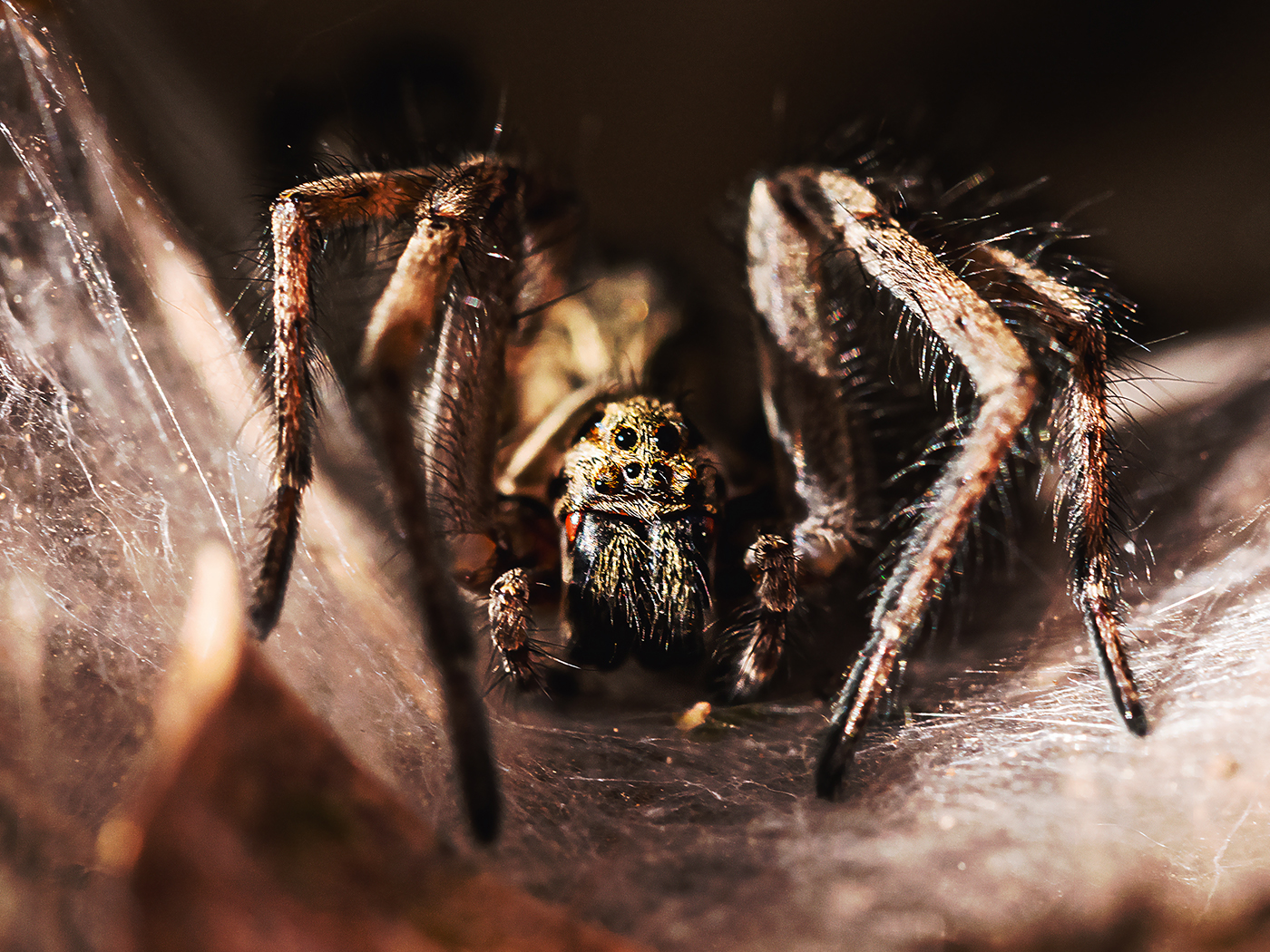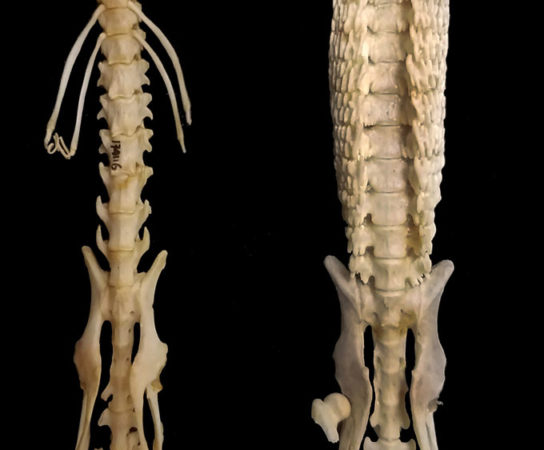
Figure 1. The spine of a hero shrew showing the interlocking vertebrae (right) compared to a more typical spine of an African giant shrew (left).
Image credit: S. Smith
Nothing else in the animal kingdom contains the extreme spinal structure and strength of hero shrews.2 Their highly unique and unusual backbones can withstand the weight of a full-grown human standing on top them. The hero shrew’s spine has interlocking vertebrae that make it extremely strong and rigid when it is compressed (Figure 1). Interestingly, the shrew’s backbone is flat on both the top and underneath. It also features plentiful amounts of broad side flanges that have lots of finger-like projections forming a nearly circular cage around the entire spine (Figure 2).
To more fully ascertain how the design of this structure gives the hero shrew its amazing spinal powers, scientists used a 3-D X-ray technology to scan the internal features of vertebrae using 20 different specimens.1 For a comparison, they also included scans from a goliath shrew that is similar in size to the hero shrew, but the goliath shrew has a standard mammalian backbone. The goal was to analyze the density and cellular structure of the interior of the bones and then combine that analysis with the morphology data of the outward mechanics of the spine.
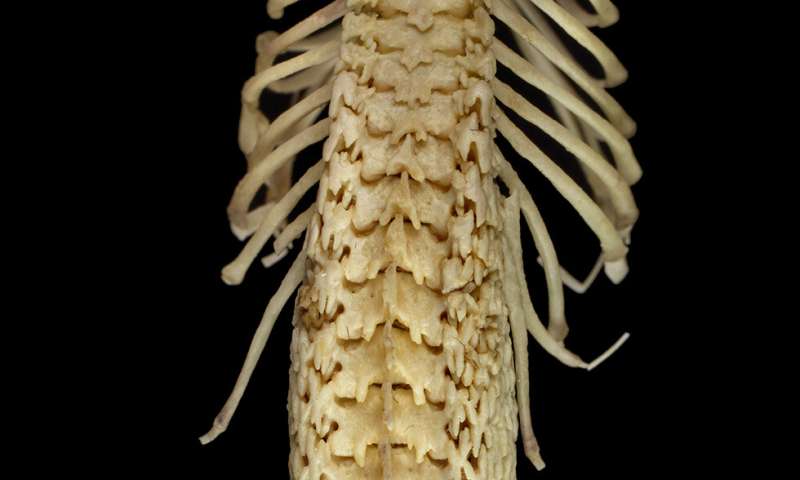

Figure 2. Hero shrew spine, viewed from underneath.
The bottom line is that hero shrew spines don't just look tough and formidable from the outside, but their inside cellular structure is highly designed to maximize strength as well. Optimization is a hallmark of design.
What purpose this unique overall design is serving the shrew has yet to be determined since little is known about the behavior of these creatures in the wild. One hypothesis is that this trait facilitates foraging for food by allowing the shrew to scrunch up and then push and force its way through difficult places to get at insects for lunch.
Unique adaptive designs in shrews and other creatures continue to amaze biologists. And of course, evolutionists have no clue as to how these highly complex and optimized all-or-nothing traits could have appeared suddenly with no evolutionary precursor. The obvious conclusion is that an all-powerful and omnipotent Creator engineered these creatures from the beginning.
Stage image: A hero shrew (Scutisorex) from the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Stage image credit: Julian Kerbis Peterhans/ScienceNews. Copyright © 2020. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
References
1. Smith, S.M. and K.D. Angielczyk. 2020. Deciphering an extreme morphology: bone microarchitecture of the Hero Shrew backbone (Soricidae: Scutisorex). Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 287: 20200457.
2. Stanley, W.T. et al. 2013. A new hero emerges: another exceptional mammalian spine and its potential adaptive significance. Biology Letters. 9: 20130486.
*Dr. Tomkins is Life Sciences Director at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his doctorate in genetics from Clemson University.