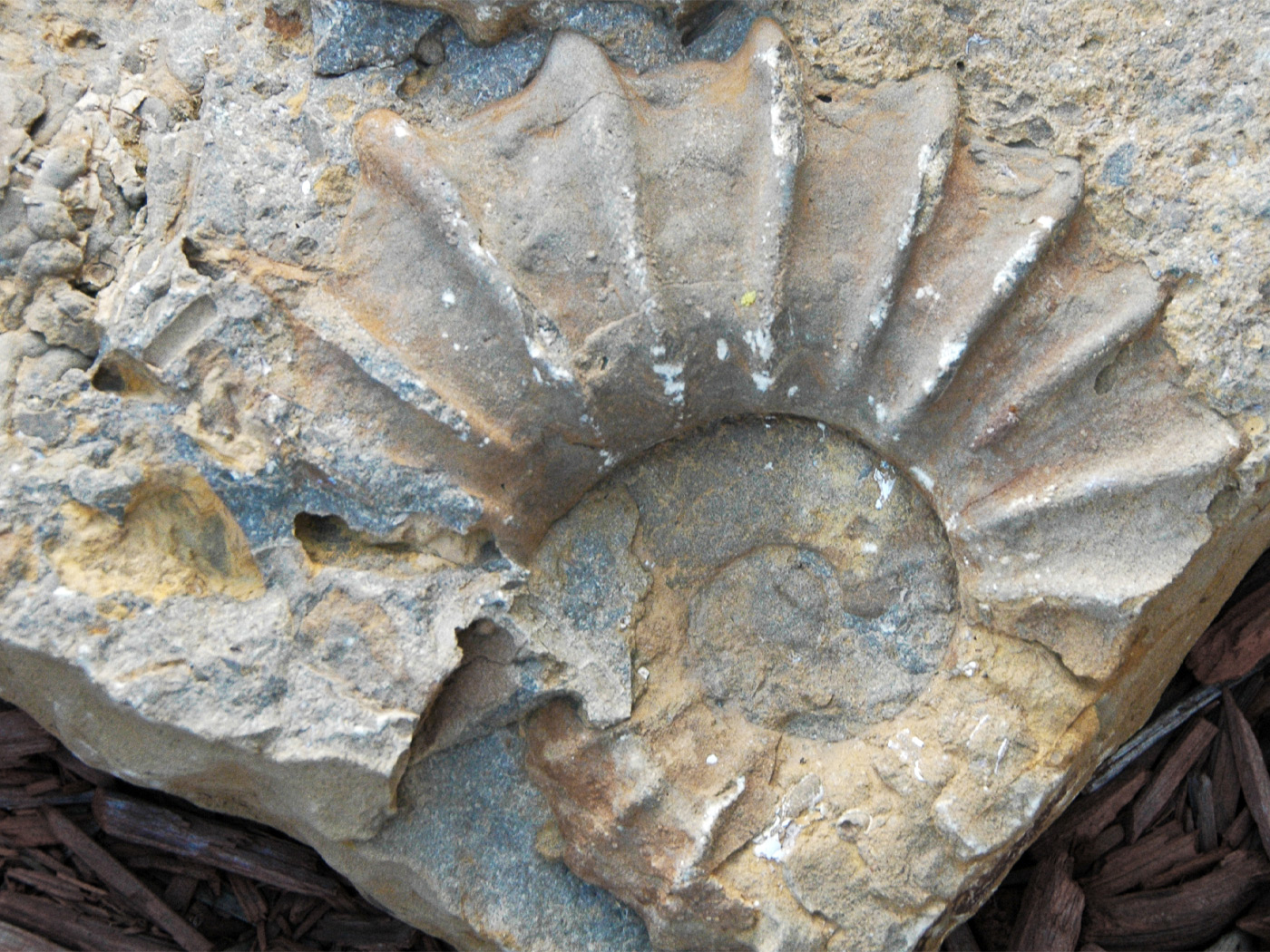
Cladarosymblema narrienense
Image credit: Flinders University
The Flinders University zoologists declared Cladarosymblema was an evolutionarily advanced member of the group called the megalichthyids (“prehistoric” lobe-finned fishes). They used “Australia’s largest cabinet CT scanner, located at Flinders University’s Tonsley campus, as well as the Australian Synchrotron in Melbourne, [allowing] researchers to unlock new data from this fossil.”1 And what exactly was this data? Evidently not much.
A cranial endocast (mold of the internal cavity of this fish’s unusually large skull) gives clues as to the shape of the brain of this animal. The area for the pituitary gland (so-called the ‘master gland’) is relatively large, suggesting a significant role in regulating various important endocrine glands.”3
That’s it? Recall Sagan’s statement. What the evidence shows is a minor variation in brain size greatly extrapolated by evolutionists to be a supposed adaptation for life on land. What about the rest of the Cladarosymblema fossil?
New information obtained from often unseen internal bones has been revealed in these scans—particularly in the gill arch skeleton, the shoulder girdle and the palate bones (the upper mouth roof area).1
It’s always good to glean new information, of course. That’s what science is all about. But do these three anatomical structures support Cladarosymblema’s preparation for transitioning from water onto land? The article doesn’t say. Skeptics of Darwinism would like to see the pelvis and associated fins/legs of this fossil.4 Do they reveal a morphology preparing the fish for land?5 In other words, is there fossil evidence documenting the appearance and “enlargement of the pelvic girdle and its firm attachment to the vertebral column via the ilium and sacral rib”6 preparing for the attachment of the evolving fish’s ‘proto’ legs and feet? No. Such fossils are illusory.
There’s a more reasonable explanation for the similarity of the endocasts between the sarcopterygian fish and salamanders. In the pre-Flood world, sarcopterygian fish were abundant and diverse. In this assortment, one would expect to see (and measure fossil endocast) variations within this created kind. But evolutionists extrapolate such minor variation as evidence for future tetrapod appearance. It should also be emphasized that amphibians (Temnospondyli, Lepospondyli) have been designed with a different biting apparatus and less adductor muscle mass (that moves a limb) compared to their alleged fish-like sarcopterygian ancestors.
Amphibians and fish were created on Days Four and Five respectively of the creation week just thousands of years ago.7
References
1. Flinders University, 2021. Ancient fish’s brain adapted for life on the land. Phys.org. Posted on phys.org December 13, accessed December 15.
2. Sagan, C. 1980. Encyclopaedia Galactica. Cosmos: A Personal Voyage. Episode 12. PBS.
3. Flinders University, 2021. Ancient fish’s brain adapted for life on the land. Phys.org. Posted on phys.org December 13, 2021, accessed December 15. (emphasis added)
4. Sherwin, F. D.Sc. (Hon.) 2013. Paleontology’s Pelvic Puzzle. Acts & Facts. 42 (5): 16.
5. Sherwin, F. D.Sc. (Hon.) 2017. Did Fish Learn to Walk? Acts & Facts. 46 (8).
6. Benton, M. 2015. Vertebrate Paleontology. 4th edition. Wiley Blackwell. Figure 4.2.
7. Genesis 1:20-22.
* Dr. Sherwin is Research Scientist at the Institute for Creation Research. He earned an M.A. in zoology from the University of Northern Colorado and received an Honorary Doctorate of Science from Pensacola Christian College.