 Collagen is a tough, stringy protein that holds bone together like the steel belts in tires. Secular scientists struggle to explain why so many different techniques have found positive detections of collagen in fossil bones. At the heart of the scientists’ struggle lies collagen’s relatively short shelf life. Prior studies accurately measured collagen content,1 but more precisely knowing collagen’s decay rate would set a sharper outside age limit for fossils that still contain it.
Collagen is a tough, stringy protein that holds bone together like the steel belts in tires. Secular scientists struggle to explain why so many different techniques have found positive detections of collagen in fossil bones. At the heart of the scientists’ struggle lies collagen’s relatively short shelf life. Prior studies accurately measured collagen content,1 but more precisely knowing collagen’s decay rate would set a sharper outside age limit for fossils that still contain it.
New techniques for Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) could improve this level of precision. As part of my recent Ph.D. research, I applied FTIR to hundreds of artificially decayed bone samples. Some experimental results appear both in my secular dissertation, searchable through scholarly libraries, and in an upcoming ICR technical book titled Ancient and Fossil Bone Collagen Remnants. Other results we show here for the first time, and still others are under review in a secular technical journal. Here’s what we did to get the findings.

ICR partnered with the Creation Research Society’s Kevin Anderson. He and his team purchased fresh bone, cleaned and ground it, then placed it into glass vials. These were inserted into water baths set to three different temperatures. Samples were removed after a set number of days that didn’t exceed a month. After that, a Dallas-based university lab allowed us access to their benchtop FTIR to scan the samples.
One new technique in FTIR applications uses the carbonyl-to-phosphate (CO/P) ratio to estimate collagen content. Each FTIR scan shows peaks where specific chemical bonds absorb laser light. Fresh bone is packed with carbonyl bonds from its abundant collagen, giving its infrared spectra large CO peaks. Phosphate bonds represent the mineral portion of bone. They last much longer, so the P peaks stay high in both fresh and old bone. The CO/P ratio lessens with time and decreases even faster at higher temperatures.
Another new technique standardizes bone processing for FTIR. This step controlled variations in the spectra caused by particle size differences. All experiments were replicated and all scans performed in triplicate.
I calculated and averaged the many CO/P results. I then plotted them for each of three temperatures. The resulting curves show that collagen decays fast at first, then more slowly as time passes. The curves have R2 values of around 0.90. These results indicate very little scatter and show the high precision we were seeking.
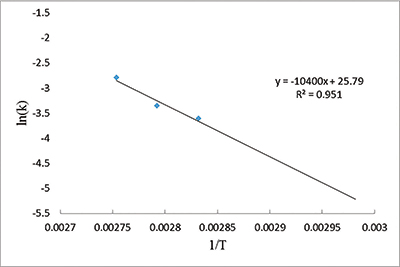
I then used the slopes to build an Arrhenius plot. The slope and intercept values of the plot help solve the Arrhenius equation, which relates temperature to the rate of a chemical process, in this case the reactions of collagen with oxygen and other nearby chemicals.2 We found an activation energy value for bovine bone collagen of 87 kJ/mol—half of a previously published experimental result of 173 kJ/mol.3 Our lower value implies even less energy is needed to decay collagen. It should decay even faster than scientists originally thought.
For example, bovine bone collagen held at 59°F would decay with a half-life of 21,012 years under ideal conditions. At that rate, collagen would not last even one million years. If Noah’s Flood deposited the fossils only 4,500 or so years ago as the Bible indicates, then we might expect some biomaterial to remain. No wonder scientists keep finding collagen in fossils.
References
- For example, Collins, M. J. et al. 1995. A Basic Mathematical Simulation of the Chemical Degradation of Ancient Collagen. Journal of Archaeological Science. 22 (2): 175-183.
- We used the form k = Ae-Ea/(RT), where k is the rate, A is a collision constant, e is the base of natural logarithms, Ea is the energy of activation, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature. Our experimental results produce Ea and A. The Arrhenius equation to calculate a collagen decay rate for any given temperature.
- Buckley, M. and M. J. Collins. 2011. Collagen survival and its use for species identification in Holocene-lower Pleistocene bone fragments from British archaeological and paleontological sites. Antiqua. 1 (1): e1.
* Dr. Thomas is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in paleobiochemistry from the University of Liverpool











