by Frank Sherwin, M.A., & Brian Thomas, M.S. *
A new dinosaur fossil discovered in China supposedly indicates that it had feathers. The Christian Science Monitor reported that the fossil of the Yutyrannus huali, the “beautiful feathered tyrant,” was the largest yet found of the now famous Chinese “feathered dinosaurs.”1 The technical description published in Nature claimed that a “gigantic feathered dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China” was recovered.2 But do these fossils really reveal former feathers, or does another interpretation, perhaps something as simple as decayed skin fibers, better explain them?
Below its headline, the Christian Science Monitor qualified the “feathered” label: These “feathers” are actually just “feather-like features,” or “simple filaments.”1 Similarly, the Nature text described them as “filamentous integumentary [skin] structures.”2 Real bird feathers are complicated, with semi-hollow cores and branching barbs, but the fossil’s filaments apparently did not have these features. If the word “feather” just means “filament,” then could any filament—like a hair or plant fiber—not also be called a “feather”?
 Answering this correctly is important. Why would God have placed feathers on dinosaurs when, today at least, only birds have feathers? On the other hand, “The idea of protofeathers [feather-like filaments on dinosaurs] has strengthened the resolve of many palaeontologists that birds are direct descendents of theropod [lizard-hipped, three-toed] dinosaurs,” even though these “feathers” have been discovered on non-theropod dinosaurs, too.3
Answering this correctly is important. Why would God have placed feathers on dinosaurs when, today at least, only birds have feathers? On the other hand, “The idea of protofeathers [feather-like filaments on dinosaurs] has strengthened the resolve of many palaeontologists that birds are direct descendents of theropod [lizard-hipped, three-toed] dinosaurs,” even though these “feathers” have been discovered on non-theropod dinosaurs, too.3
Also, neither dinosaur skin impressions nor original dinosaur skin has follicles similar to those that produce feathers in bird skin.4 What purpose would bird feathers serve on those tough dino hides? Plus, dinosaurs could not have evolved into birds because transmutating a dinosaur skeleton into a bird skeleton would have rendered the transitional creatures unfit, being unable to fly or walk properly.5 These Chinese tyrannosaur fibers, as with perhaps all the famous Chinese fossil dinosaur “feathers” so far, are more straightforwardly interpreted as the fossilized fragments of partly decayed skin.

Skin contains collagen protein fibers that decay more slowly than the soluble biomaterials that surround them. The famous Chinese dinosaurs probably began rotting as they were transported by the waters of Noah’s Flood only 4,500 or so years ago, even as modern carcasses rot. The soluble flesh rotted first. The thickly woven collagen fibers would have soon rotted, too, but the surrounding mud or wet sand quickly turned to dry rock that inhibited growth of collagen-eating microbes.
Researchers in 2005 found an excellent match between partially decayed skin from a variety of animal carcasses and dinosaur “feathers” then published. Even the evolutionary authors contended that calling dinosaur fibers “feathers” was “misleading.”6 And these new tyrannosaur fibers provide no evidence to overturn that analysis.
The idea that dinosaurs evolved into birds is also misleading. The poster child of Darwinian change is Archaeopteryx, an alleged link via therapod dinosaurs between reptiles and birds. However, unlike dinosaurs, Archaeopteryx had a large braincase for the increased motor control and sensory input that were required for flight. Theropods had a lizard-like pelvis that was distinct from a bird’s frame. Furthermore, Archaeopteryx had a robust furcula (wishbone), a trait characteristic of strong fliers—one that keeps flight muscles from crushing the bird’s delicate internal air sacs. No evidence supports the story that such fully formed wings with fused clavicles “evolved from” the tiny, clavicle-free theropod forelimbs. Even claw measurements of Archaeopteryx fall within the range of true perching birds.7 It was a bird without a single transitional feature.
In addition, those who insist that dinosaurs evolved into birds have to willfully ignore the fossil bird prints found in rock layers containing some of the “earliest” dinosaurs—the supposed ancestors of birds.8
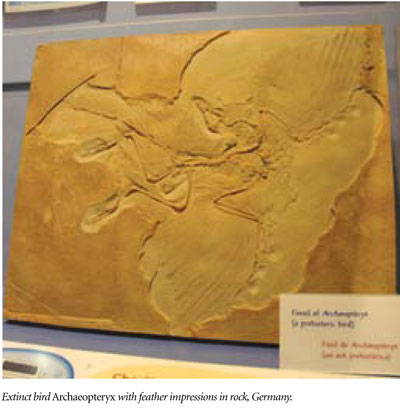

An Archaeopteryx bird fossil from Solnhofen, Germany, was recently analyzed using new techniques that detect element ratios without destroying the material. The results indirectly, but certainly, identified original feather and bone proteins. It had the same biochemistry that comprises today’s feathers.9 Fossils show no evolution of feathers.
The original Archaeopteryx tissue also showed how young it must be. Its evolutionary age assignment is about 150 times older than its protein decay age estimate. So, not only does it look purposefully created, but it also appears to be recently fossilized. A separate study found that the supposed “feather” filaments in another Chinese dinosaur from the same large fossil set as that containing this new tyrannosaur, called the Jehol Biota, were also original biochemicals.10, 11 They could persist in this state for perhaps hundreds of thousands of years, but after a million or so years they would have spontaneously degraded to dust.
A feathered dinosaur may someday be discovered. But even then, feathers on a dinosaur would not solve evolution’s biophysical impasse of converting a reptile skeleton into that of a bird. And so far, the evidence for feathered dinosaurs is much better interpreted as decayed skin fibers. Overall, fossils show that dinosaurs and birds have always been separate creatures.12 And this is exactly what one would expect if dinosaurs and birds were created separately, each to reproduce “after their kind.”13
References
- Spotts, P. Dressed to kill: A feathered tyrannosaur is discovered in China. Christian Science Monitor. Posted on csmonitor.com April 4, 2012, accessed April 5, 2012.
- Xu, X. et al. 2012. A gigantic feathered dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of China. Nature. 484 (7392): 92-95.
- Lingham-Soliar, T., A. Feduccia and X. Wang. 2007. A new Chinese specimen indicates that ‘protofeathers’ in the Early Cretaceous theropod dinosaur Sinosauropteryx are degraded collagen fibres. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 274 (1620): 1823-1829.
- Thomas, B. Mummified Dinosaur Skin Looks Young. ICR News. Posted on icr.org July 30, 2009, accessed April 26, 2012.
- Thomas, B. Fixed Bird Thigh Nixes Dino-to-Bird Development. ICR News. Posted on icr.org June 22, 2009, accessed August 19, 2011.
- Feduccia, A., T. Lingham-Soliar and J. R. Hinchliffe. 2005. Do Feathered Dinosaurs Exist? Testing the Hypothesis on Neontological and Paleontological Evidence. Journal of Morphology. 266: 134.
- Feduccia, A. 1993. Evidence from Claw Geometry Indicating Arboreal Habits of Archaeopteryx. Science. 259 (5096): 790-793.
- Melchor, R. N., S. de Valais, and J. F Genise. 2002. Bird-like fossil footprints from the Late Triassic. Nature. 417(6892): 936.
- Bergmann, U. et al. 2010. Archaeopteryx feathers and bone chemistry fully revealed via synchrotron imaging. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (20): 9060-9065.
- Zhang, F. et al. 2010. Fossilized melanosomes and the colour of Cretaceous dinosaurs and birds. Nature. 463(7284): 1075-1078.
- Lingham-Soliar, T. 2011. The evolution of the feather: Sinosauropteryx, a colorful tail. Journal of Ornithology. 152(3): 567-577.
- Oard, M. 2012. Did Birds Evolve from Dinosaurs? Dinosaur Challenges and Mysteries. Atlanta, GA: Creation Book Publishers, 144-155.
- Genesis 1:25.
* Mr. Sherwin is Research Associate, Senior Lecturer, and Science Writer, and Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Cite this article: Sherwin, F. and B. Thomas. 2012. Did Some Dinosaurs Really Have Feathers? Acts & Facts. 41 (6): 16-17.









