Zookeepers in Reynosa, Mexico, recently witnessed a female zebra give birth to a "zonkey." So far, this rare hybrid animal appears to be in good health.1 Meanwhile, an Irish farmer's sheep chases its baby "geep," sired by a goat.2 What do zonkeys and geeps have to do with Noah's Ark?
The zebra mother had grown familiar with a neighboring dwarf albino donkey. Although its father was colorless, the zonkey progeny has striped legs and a mostly brown torso.1 Zebras and donkeys actually have different numbers of chromosomes, making fertilization quite challenging, but cellular machinery sometimes somehow finds a way to form a viable offspring. It appears life was designed to do just that.
Similarly, the typical goat has 60 chromosomes, and most domestic sheep have but 54. Modern science has attached separate genus names for the two varieties, but the fact that they can interbreed demonstrates that they descended from a single kind. They both fall under a broader category: the subfamily called "Caprinae."
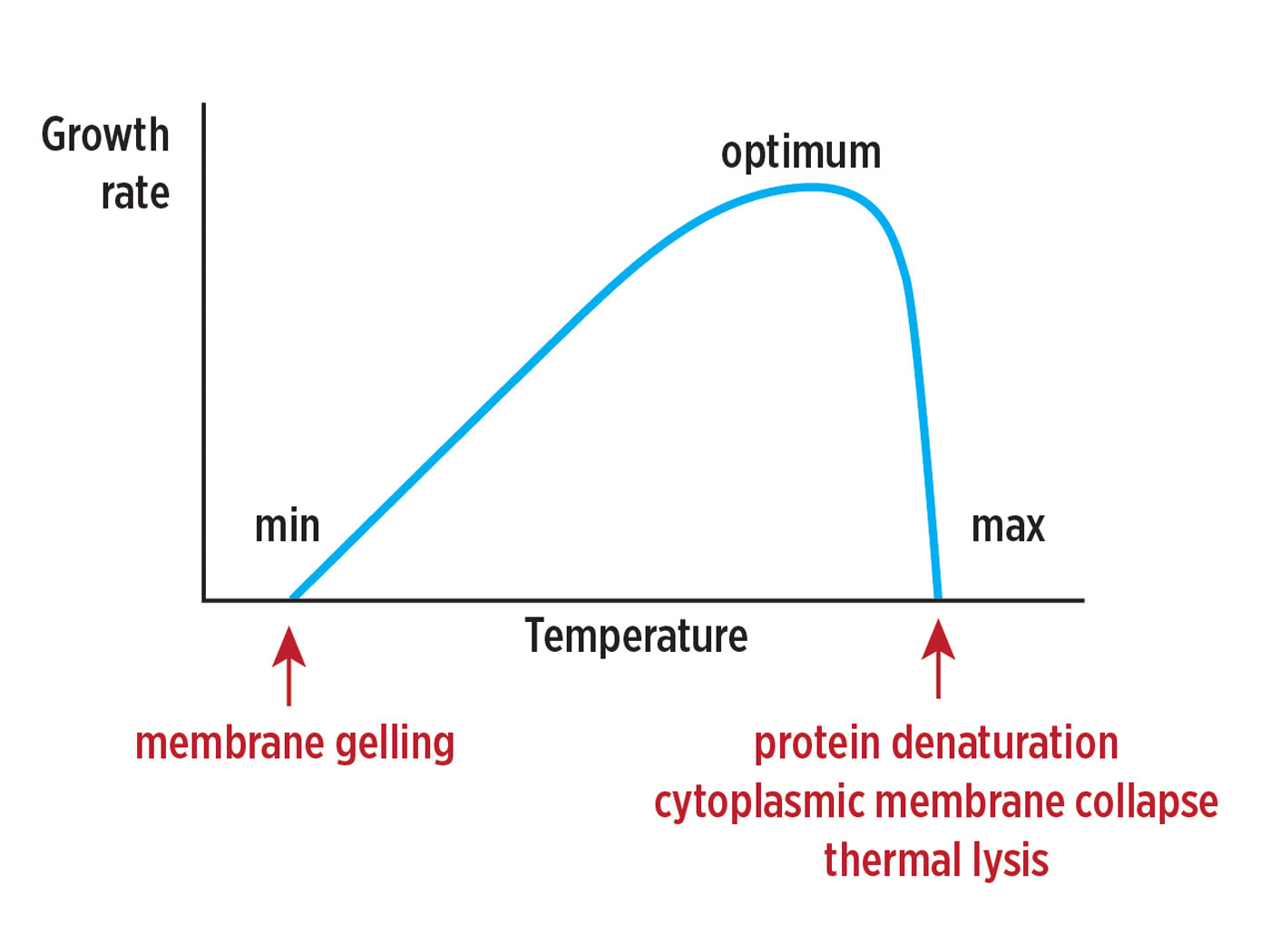
Family names, or in this case the subfamily, for animals seems to best approximate the Genesis kind. Adding those of air-breathing, land-dwelling animals yields a population that would not even take up half the Ark's calculated volume.3
Nevertheless, Bible skeptics discount the Ark, insisting that it could not possibly have carried all the required creatures. When asked to estimate how many creatures entered the vessel, they sometimes suggest millions—an unrealistic number by far. But they sometimes add sea creatures to their tallies, and they may also be counting various versions of sheep, goats, zebras, donkeys, and horses separately.
Noah and his sons only needed two of each kind, and if two creatures can interbreed, they essentially belong to the same kind. Noah's family also only needed land-dwelling, air-breathing animals. The text says, "Of the birds after their kind, of animals after their kind, and of every creeping thing of the earth after its kind, two of every kind will come to you to keep them alive."4 That rules out fish and a host of other water creatures, which comprise the largest chunk of currently tallied animal names—Nemo and Flipper need not apply.
How did today's animal varieties arise, anyway? Since creatures continue to diversify into newly named varieties as they pioneer new environments and breed with neighbors of their own general kind, it stands to reason that the few number of animals on the ark rapidly diversified after the Flood into the vastly diverse animal kingdom we see today. For example, over a thousand named species of finches and sparrows have been linked through breeding studies to a single, interbreeding kind.5 And that's where rare animals like zonkeys and geeps come in, showing that today's varieties trace back to basic kinds.
Were horses, zebras, donkeys, sheep and goats on the ark separately? Maybe, but based on these rare cross breeds, perhaps the two basic kinds were represented by animals that looked more like zonkeys and geeps.
References
- Rare Zonkey Born in Mexico Zoo. ABC News. Posted on abcnews.go.com April 25, 2014, accessed April 28, 2014.
- Meet the Geep, a Goat-Sheep Hybrid Born in Ireland. ABC News. Posted on abcnews.go.com April 25, 2014, accessed April 29, 2014.
- Woodmorappe, J. 1996. Noah's Ark: A Feasibility Study. Santee, CA: Institute for Creation Research, 16.
- Genesis 6:20.
- Lightner, J. 2010. Identification of a large sparrow-finch monobaramin in perching birds (Aves: Passeriformes). Journal of Creation. 24 (3): 117-121.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on May 7, 2014.