Last month we showed preliminary evidence suggesting that the molecular patterns we see in animal species may be due to different rates of mutation in each “kind.”1 Further investigation of the match between mutation rates and genetic differences among species suggests that this initial hypothesis was incorrect.
Our initial hypothesis posited that individual gene sequences were identical in each kind but that the overall genome sequences were different. This hypothesis was consistent with the common design principle of tool re-use—if a tool performs a function well, good engineers re-use it for other applications. Conversely, in the genome, genes may act like tools in the construction (development) of each creature; if so, they might be re-used for the same function in many different creatures. Our hypothesis was also consistent with the common assumption that mitochondrial genes (that we were investigating) were “housekeeping”—they performed the same function in every creature. Hence, there seemed to be no functional reason for designing these gene sequences differently in different kinds.
We also hypothesized that, from this originally created gene sequence identity, modern gene sequence differences arose as a result of different rates of genetic change over time. These differences in rates would eventually produce a hierarchy of differences among modern species.
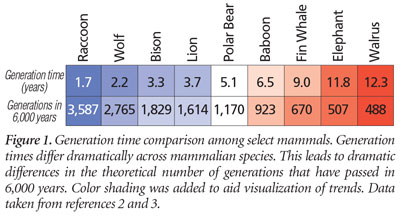 To test our hypothesis, we used a surrogate measure of mutational change, the generation time (the time from conception to sexual maturity) for each species. Since preservation of any mutation in a population depends on successful transfer of the mutation to progeny, the mutation rate for a species is intimately tied to the species’ generation time.
To test our hypothesis, we used a surrogate measure of mutational change, the generation time (the time from conception to sexual maturity) for each species. Since preservation of any mutation in a population depends on successful transfer of the mutation to progeny, the mutation rate for a species is intimately tied to the species’ generation time.
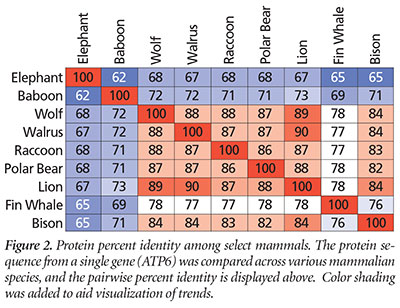 Our recent analyses and ranking of mammalian generation times revealed trends that were inconsistent with our original hypothesis. The trends we observed in genetic similarity did not match the trends in species’ generation times. For example, compare the data in Figure 1 and Figure 2 (representing a small subset of our comparisons). In Figure 1, raccoons and walruses mark the extremes in reproductive rates. The differential mutation rate hypothesis would predict these two species to be very different genetically due to the high reproductive rate in raccoons. However, in genetic terms, these two species have one of the highest percent identity values (Figure 2). This result was inconsistent with our hypothesis. Conversely, elephant and baboon do not differ dramatically in their generation time (Figure 1), and the differential mutation rate hypothesis would predict high genetic similarity between them. They are among the most dissimilar genetically of the species analyzed (Figure 2). This was also inconsistent with our hypothesis and illustrates the results obtained from our larger analyses.
Our recent analyses and ranking of mammalian generation times revealed trends that were inconsistent with our original hypothesis. The trends we observed in genetic similarity did not match the trends in species’ generation times. For example, compare the data in Figure 1 and Figure 2 (representing a small subset of our comparisons). In Figure 1, raccoons and walruses mark the extremes in reproductive rates. The differential mutation rate hypothesis would predict these two species to be very different genetically due to the high reproductive rate in raccoons. However, in genetic terms, these two species have one of the highest percent identity values (Figure 2). This result was inconsistent with our hypothesis. Conversely, elephant and baboon do not differ dramatically in their generation time (Figure 1), and the differential mutation rate hypothesis would predict high genetic similarity between them. They are among the most dissimilar genetically of the species analyzed (Figure 2). This was also inconsistent with our hypothesis and illustrates the results obtained from our larger analyses.
What might be the real explanation for the genetic patterns among species? Perhaps the differential mutation rate hypothesis applies to only select groups of creatures—perhaps to insects, but not to mammals. Alternatively, the explanation for the genetic patterns might be something entirely different. Perhaps God created different ATP6 sequences in different kinds, after which little diversification happened genetically—this is the subject of our current investigation.
References
- Jeanson, N. 2012. Bio-Origins Project Update, Hypothesizing Differential Mutation Rates. Acts & Facts. 41 (10): 6.
- Altman, P. and D. Dittmer, eds. 1972. Biology Data Book, Vol. 1, 2nd ed. Bethesda, MD: Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
- Grzimek, H. C. B., ed. 1972. Grzimek’s Animal Life Encyclopedia. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, Inc.
* Dr. Jeanson is Deputy Director for Life Sciences Research and received his Ph.D. in Cell and Developmental Biology from Harvard University.
Cite this article: Jeanson, N. 2012. Bio-Origins Project Update, Evidence Against Differential Mutation Rates. Acts & Facts. 41 (11): 6.














