Scientists made a virtual microbe, complete with dozens of interconnected cell functions. But it wasn't easy. Their creation could be used in two important areas of research.
The Stanford-led team of bioengineers watched 128 of their digital cells, referred to as being in silico, grow in cyberspace.1 The in silico cells behaved similarly to the real live Mycoplasma bacteria after which they were modeled. Biomedical research may one day use digital cells to estimate how real cells respond to different drugs or conditions.
Publishing in the journal Cell, the study authors wrote, "Our model is based on a synthesis of over 900 publications and includes more than 1900 experimentally observed parameters."1 They first used differing algorithms to represent each of 28 diverse cellular processes, like DNA synthesis and repair, RNA processing, and protein modification and transport.
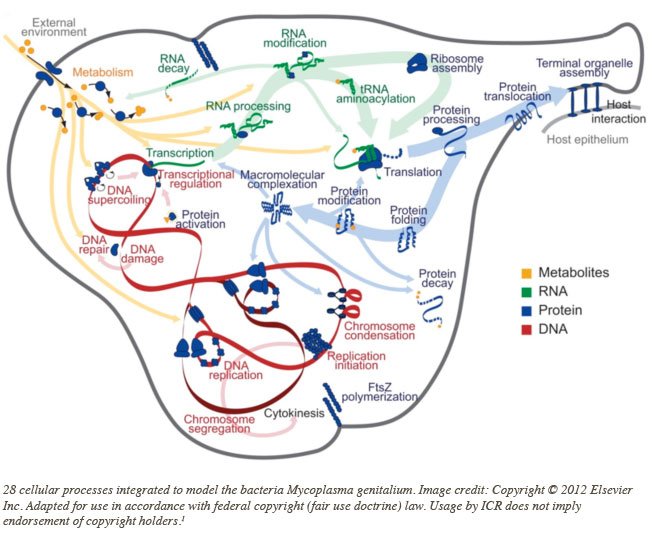
How could they then unify so many different features? "The current effort involved so many different cellular functions and mathematical representations that a more general approach was needed."1
They placed the 28 virtual functions under a simulation algorithm that processed the input and output of each. Their result was the world's first complete virtual germ. Only it's not totally complete. The study authors wrote, "The model presented here is a 'first draft,' and extensive effort is required before the model can be considered complete."1
Why would they suggest even more extensive effort than that which they already gave? They wrote, "The technical and modeling aspects of this study will also have to be expanded, updated, and improved as new knowledge comes to light." And all of this to model the bacterium with the world's smallest genome.
Only a few years ago, Mycoplasma was thought to be the simplest bacteria because it uses the fewest genes. But researchers were surprised to discover that its gene and protein regulation and processing systems were far more complicated than ever expected.2 So, it makes sense that even the enormous efforts so far spent are still not enough to make even a virtual cell.
What does all of this imply for origins research?
First, with so much intelligently-directed effort required to build its virtual facsimile, researchers can rest assured that intelligently-directed effort was likewise required to build the original bacteria. This resists Darwinian doctrines that insist cells arose from nature, not intelligence.
Last, when in some future years bioengineers complete their final draft of the virtual cell, they will only succeed in building something that's not real. Although it is possible to model how molecules and maybe even whole cells behave, it is infinitely more difficult to assemble actual atoms into their correct positions to build a cell. But somebody did just that.
References
- Karr, J.R. 2012. A Whole-Cell Computational Model Predicts Phenotype from Genotype. Cell. 150 (2): 389-401.
- Thomas, B. Bacteria Study Shoots Down 'Simple Cell' Assumptions. ICR News. Posted on icr.org January 4, 2012, accessed August 13, 2012.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on August 20, 2012.



















