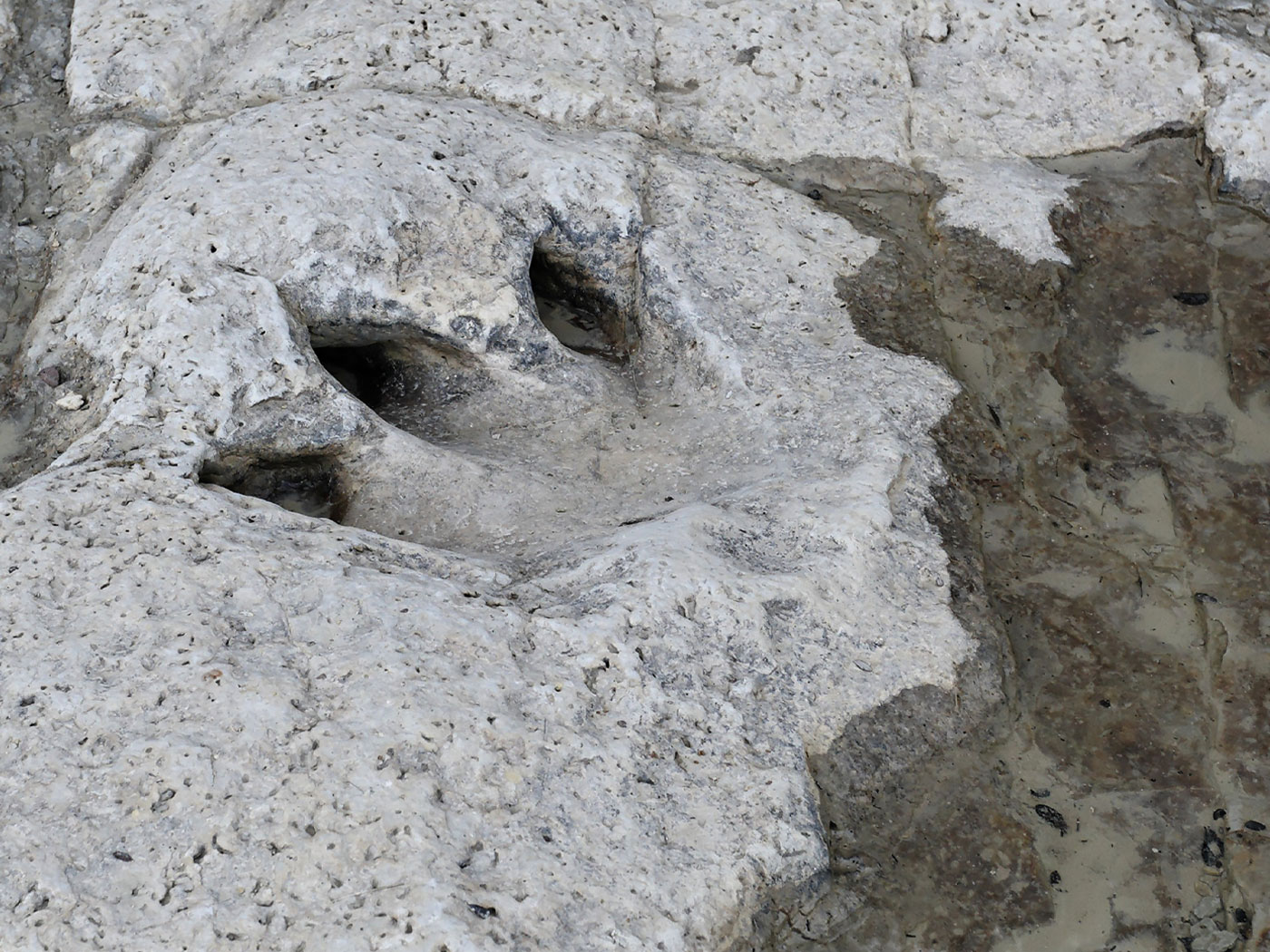
In 2008, excavations in a South African cave uncovered two red-stained abalone shell bowls along with various tools in what was evidently a workshop where ochre and other ingredients were mixed, most likely for use as paint. Researchers examined the artifacts and have published a study in which they say the artifacts are 100,000 years old. Could they really be that ancient?
According to standard evolutionary dogma, mankind did not start evolving advanced cognitive abilities until about 70,000 years ago. Christopher Henshilwood, lead author of the study that appeared in Science, told Nature News that these artifacts "push back by 20,000 or 30,000 years" the imagined advent of "complex cognition,"1 or the time when humans finally had the brainpower to prepare and use paint.
In 2001, Donald Johanson, the famed discoverer of the fossil primate "Lucy," wrote, "The archaeological picture changed dramatically around 40-50,000 years ago with the appearance of behaviorally modern humans."2 But Henshilwood said that his date for these paint-processing materials "suggests conceptual and probably cognitive abilities which are the equivalent of modern humans" (emphasis added).1
So, did man evolve modern thought capacities 40-50,000, 70,000, or 100,000 years ago? Are any of these numbers trustworthy? Not only does the 100,000-year date assignment conflict with prior evolutionary notions, but also with the straightforward 6,000 or so years of world history recorded in the Bible.
The study authors performed three different dating techniques on the remains.3 Curiously, however, they did not carbon-date any artifacts. Some of the tools included cow, seal, and dog bones, and the abalone shells must still contain protein. All of this material should have datable carbon. Why were they not carbon-dated?
The answer probably has to do with the fact that carbon dating is unreliable for artifacts older than 60,000 or so carbon-years. If any carbon-14 was detected in these remains, then the carbon age would be no more than 60,000 years, and probably far fewer—thousands of years younger than these scientists' target date.
In their Science report, the archaeologists showed dates on a photograph of several vertical feet of cave floor layers. However, one dating method showed an age of 100,000 years for a layer that was dated at only 75,000 years by another method. And there were other inconsistencies, raising suspicion over the reliability of the age assignments.4
And there is more. They labeled the very top eight-or-so-inch-thick layer "hiatus," instead of assigning it an age like the other layers. Then they labeled the next lower layer at about 68,000 years. Why would nine feet of cave sediments accumulate over 32,000 years, then almost no sediment accumulate for 68,000 years?
The idea that man evolved his cognitive abilities has no scientific support, either. Cognitive thoughts are not traits encoded by particular genes, but immaterial traits. Thoughts interact with the material world through the sophisticated architecture of the brain, which requires thousands of precisely interacting genes. Tinkering with brains or brain-developing genes brings disaster, not improvement. Thus, brain biology shows that modern human cognition must have been purposeful and present at the beginning.
The ideas that human cognition evolved and that these cave sediments are 100,000 years old are both underpinned by evolutionary dogma, not historical or scientific research. However, these paint-making tools do show that the earliest human inhabitants of what is today South Africa possessed modern human abilities—which makes sense if they had recently descended from Noah.
References
- Corbyn, Z. African cave's ancient ochre lab. Nature News. Posted on nature.com October 13, 2011, accessed October 17, 2011.
- Johanson, D. Origins of Modern Humans: Multiregional or Out of Africa? Action Bioscience: American Institute of Biological Sciences. Posted on actionbioscience.org May 2001, accessed October 18, 2011.
- Henshilwood, C. S. et al. 2011. A 100,000-Year-Old Ochre-Processing Workshop at Blombos Cave, South Africa. Science. 334 (6053): 219-222.
- Woodmorappe, J. 1999. The Mythology of Modern Dating Methods. El Cajon, CA: Institute for Creation Research.
Image credit: Copyright © 2011 AAAS. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on October 25, 2011.