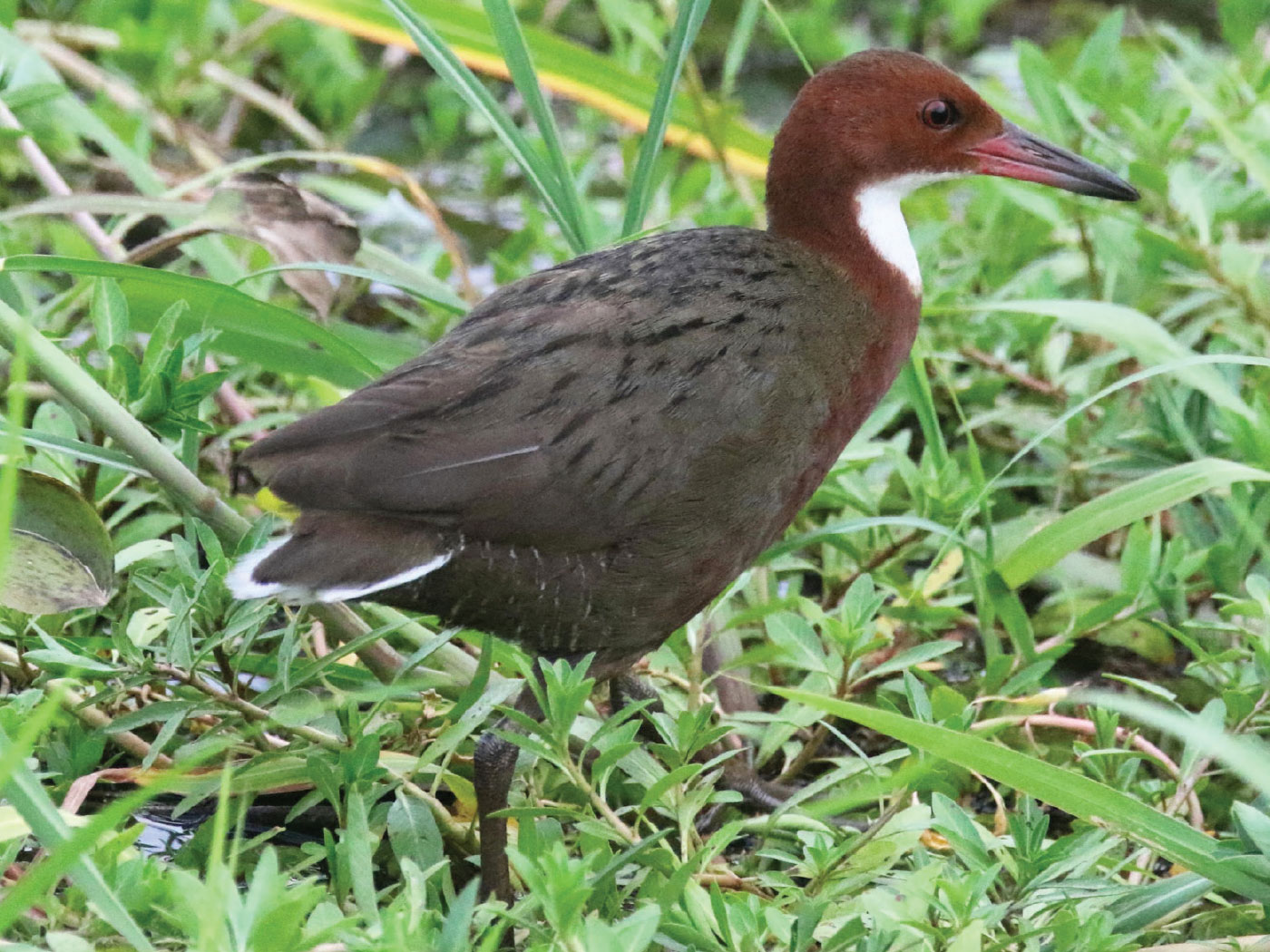
More than 80 varieties of fish, amphibian, and reptile mothers are able to lay eggs that have not been fertilized and yet produce offspring. In a process called "parthenogenesis," these eggs hatch little clones of the mother, which in turn lay clone eggs themselves. Could this remarkable mode of unisexual reproduction have evolved?
At first, instances in the animal kingdom of females producing offspring with no male involvement were thought to be quite rare, but further study has shown that more of these self-cloning animal lineages have been swimming, hopping and crawling underfoot than was previously suspected. Recently, biologists crossbred (hybridized) two species of whiptail lizards, which produced new unisexual females in the lab. How this works "remains unknown," the researchers wrote in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.1
Their female whiptail lizard was "triploid," having an extra copy of the mother lizard’s chromosomes, and she was already parthenogenetic. The father had the normal "diploid" number of chromosomes—one set from each of its parents. The study produced four new parthenogenetic "species" that also have extra sets of chromosomes (a condition called "polyploidy").
These results were quite unexpected, considering that for decades, deliberate attempts to hybridize whiptail lizards in efforts to produce a new self-cloning population have resulted in sterile offspring. Wired Science reported that senior author Peter Baumann of the Stowers Institute for Medical Research "wonders if some lizard lineages might actually alternate between sexual and unisexual reproduction, depending on the pressures of each era."2
This possibility is intriguing, though doubtless any potential for lizards to switch reproductive modes depends less on "pressures" and more on internal programming. It would make sense that a Creator would have endowed these egg-laying vertebrates with the potential to perpetuate themselves even in the event that a male was unavailable.
A study of toads in Krygyzstan, for example, found that their ability to form polyploids has "reciprocal origins," occurring as a result of crosses and back-crosses between toads of different numbers of chromosome sets.3 Since polyploidy is linked to parthenogenesis, it is possible that both phenomena are made possible by intricate and purposively engineered reproductive systems.
The fact that parthenogenesis works implies that these creatures were originally outfitted with the biochemical equipment to facilitate two separate modes of reproduction: sexual and unisexual. In contrast, evolution has no useful explanation for the origin of sexual reproduction, let alone unisexual.4
References
- Lutes, A. A. et al. Laboratory synthesis of an independently reproducing vertebrate species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Published online before print May 4, 2011.
- Keim, B. All-Female Lizard Species Created in Lab. Wired Science. Posted on wired.com May 3, 2011, accessed May 18, 2011.
- Stöck, M., et al. 2009. A Vertebrate Reproductive System Involving Three Ploidy Levels: Hybrid Origin of Triploids in a Contact Zone of Diploid and Tetraploid Palearctic Green Toads (Bufo Viridis Subgroup). Evolution. 64 (4): 944-959.
- Harrub, B. and Thompson, B. 2004. The origin of gender and sexual reproduction. Journal of Creation (formerly TJ). 18 (1): 120-127.
Image credit: William B. Neaves
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on May 25, 2011.