Humans and great apes differ in chromosome numbers—humans have 46 while apes have 48. The difference is claimed to be due to the “end-to-end fusion” of two small, ape-like chromosomes in a human-ape ancestor that joined in the distant past and formed human chromosome 2. This idea was first proposed by researchers who noticed that humans and chimps share similar chromosomal staining patterns when observed under a microscope.1 However, humans and chimps also have regions of their chromosomes that do not share common staining patterns.
Supposed proof for the alleged fusion came in 1991, when researchers discovered a fusion-like DNA sequence about 800 bases in length on human chromosome 2.2 However, it was unexpectedly small in size and extremely degenerate. More importantly, this new fusion-like sequence wasn’t what the researchers were expecting to find since it contained a signature never seen before. All known fusions in living animals are associated with a sequence called satellite DNA (satDNA) that fuses in one of the two following scenarios: 1) satDNA-satDNA or 2) satDNA-telomereDNA. (Telomeres are the regions at the end of chromosomes that contain thousands of repeats of the DNA sequence “TTAGG.”)3,4 The alleged fusion sequence contained a different signature, a telomere-telomere fusion, and, if real, would be the first documented case ever seen in nature.
In 2002, 614,000 bases of DNA surrounding the fusion site were fully sequenced, revealing that the alleged fusion sequence was in the middle of a gene originally classified as a pseudogene because there was not yet any known function for it.5,6 The research also showed that the genes surrounding the fusion site in the 614,000-base window did not exist on chimp chromosomes 2A or 2B—the supposed ape origins location. In genetics terminology, we call this discordant gene location a lack of synteny.
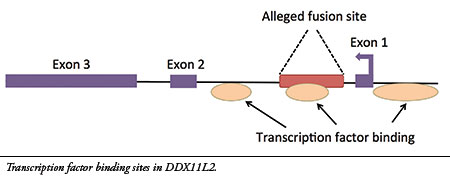 I have now published new research on the alleged fusion site, revealing genetic data that fully debunk its evolutionary claims.7 My analysis confirms that the site is located inside a gene called DDX11L2 on human chromosome 2. Furthermore, the alleged fusion sequence contains a functional genetic feature called a “transcription factor binding site” that is located in the first intron (non-coding region) of the gene (see illustration). Transcription factors are proteins that bind to regulatory sites in and around genes to control their function, acting like switches. The DDX11L2 gene has three of these areas, one of which is encoded in the alleged fusion site.
I have now published new research on the alleged fusion site, revealing genetic data that fully debunk its evolutionary claims.7 My analysis confirms that the site is located inside a gene called DDX11L2 on human chromosome 2. Furthermore, the alleged fusion sequence contains a functional genetic feature called a “transcription factor binding site” that is located in the first intron (non-coding region) of the gene (see illustration). Transcription factors are proteins that bind to regulatory sites in and around genes to control their function, acting like switches. The DDX11L2 gene has three of these areas, one of which is encoded in the alleged fusion site.
Chromosomes are double-stranded DNA molecules and contain genes on both strands that are encoded in opposite directions. Because the DDX11L2 gene is encoded on the reverse-oriented strand, it is read in the reverse direction (see Exon 1 arrow). Thus, the alleged fusion sequence is not read in the forward orientation typically used in literature as evidence for a fusion—rather, it is read in the reverse direction and encodes a key regulatory switch.
The supposed fusion site is actually a key part of the DDX11L2 gene. The gene itself is part of a complex group of RNA helicase DDX11L genes that produce regulatory long non-coding RNAs. These DDX11L2 RNA transcripts are produced in at least 255 different cell types and tissues in humans, highlighting the genes’ ubiquitous biological function.
Functional genes like DDX11L2 do not arise by the mythical fusing of telomeres. The alleged fusion site is not a degenerate fusion sequence but is and, since creation, has been a functional feature in an important gene.7
References
- Yunis, J. J. and O. Prakash. 1982. The origin of man: A chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science. 215 (4539): 1525-1530.
- Ijdo, J. W. et al. 1991. Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 88 (20): 9051-9055.
- Tsipouri, V. et al 2008. Comparative sequence analyses reveal sites of ancestral chromosomal fusions in the Indian muntjac genome. Genome Biology. 9 (10): R155.
- Adega, F., H. Guedes-Pinto and R. Chaves. 2009. Satellite DNA in the karyotype evolution of domestic animals—clinical considerations. Cytogenetics and Genome Research. 126 (1-2): 12-20.
- Fan, Y. et al. 2002. Gene Content and Function of the Ancestral Chromosome Fusion Site in Human Chromosome 2q13-2q14.1 and Paralogous Regions. Genome Research. 12 (11): 1663-1672.
- Fan, Y. et al. 2002. Genomic Structure and Evolution of the Ancestral Chromosome Fusion Site in 2q13-2q14.1 and Paralogous Regions on Other Human Chromosomes. Genome Research. 12 (11): 1651-1662.
- Tomkins, J. 2013. Alleged Human Chromosome 2 “Fusion Site” Encodes an Active DNA Binding Domain Inside a Complex and Highly Expressed Gene—Negating Fusion. Answers Research Journal. 6: 367-375.
* Dr. Tomkins is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and received his Ph.D. in genetics from Clemson University.