A research team described a form of fossilization that it thinks can explain how original proteins have lasted for millions of years in Earth’s crust. It does match certain fossil features, but leaves two key questions unanswered. And that leaves soft tissue fossils still looking quite young.
Publishing in Nature Communications, Yale University scientist Jasmina Wiemann and colleagues drew two parallels between the soft tissues they found in fossils and tissues they toasted on a hot plate in the lab.1 First, both had darker coloration. This happens often, for example when apple slices darken when left out on the counter. Second, both real and artificial fossils showed similar infrared spectra. These spectra indicate the chemistry of a given sample. In this case, the spectra showed that proteins had crosslinked to form polymers.
Despite the fact these dark polymers are no longer proteins, they keep the shape of the original tissue. The research results agreed with this, but then the study authors slid into storytelling. According to their toast model of soft tissue fossil preservation, these polymers shield nearby proteins from microbes and even chemical interactions.
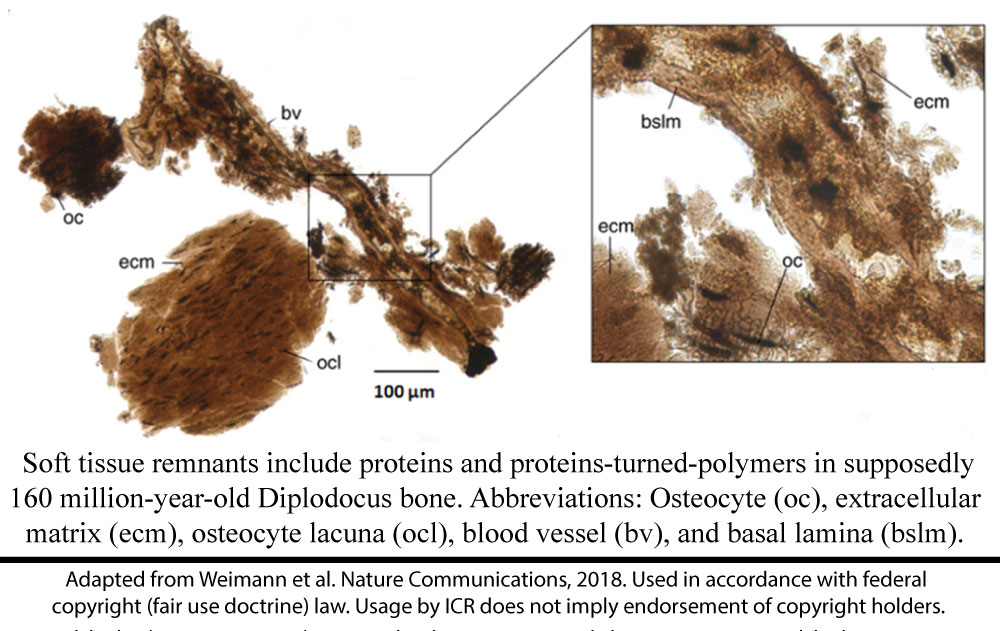 How did the team reach the conclusion that this shield somehow stays in place for over 150 million years? First, they did it by assuming that the fossils’ proteins and polymers had been lying in the ground with almost no decay for millions of years. This begs the question of how long the fossils have been there. A longevity experiment would have been the proper way to show how long these organic molecules could last, but the study presented no such experiment.
How did the team reach the conclusion that this shield somehow stays in place for over 150 million years? First, they did it by assuming that the fossils’ proteins and polymers had been lying in the ground with almost no decay for millions of years. This begs the question of how long the fossils have been there. A longevity experiment would have been the proper way to show how long these organic molecules could last, but the study presented no such experiment.
A second unanswered question comes from entirely soft tissues, with no crusty coating, found in certain fossils. For example, University of North Carolina paleontologist Mary Schweitzer recorded video of T. rex connective tissue being pulled, stretched, and flexing back into shape.2 Armitage and Anderson later published their description of a pliable sheet of soft tissue extracted from a Triceratops horn core excavated from near the surface of the ground.3
The idea that fossil material could have remained entirely flexible and original for 551 million years is laughable. ![]()
But a Precambrian sea floor worm sheath takes the longevity prize. The idea that fossil material could have remained entirely flexible and original for 551 million years is laughable. Publishing in the Journal of Paleontology, the study authors wrote, “Minerals have not replicated any part of the soft tissue and the carbonaceous material of the wall is primary [not replaced], preserving the original layering of the wall, its texture, and fabrics.” They described the worm sheath as still “flexible, as shown by its soft deformation.”4 No dark, crusty toast there.
The toast model has a few merits, but ultimately swaps bad logic for a decay experiment and ignores non-toasted, still-soft proteins in fossils. Back to the drawing board—the toast model belongs back on the hot plate.
References
1. Wiemann, J. et al. 2018. Fossilization transforms vertebrate hard tissue proteins into N-heterocyclic polymers, Nature Communications. 9: 4741.
2. B-Rex. 60 Minutes. Aired on CBS November 15, 2009. Posted on youtube.com December 26, 2010.
3. Armitage, M. H., and K. L. Anderson. 2013. Soft sheets of fibrillar bone from a fossil of the supraorbital horn of the dinosaur Triceratops horridus. Acta Histochemica. 115(6): 603-608.
4. Moczydlowska, M., F. Westall, F. Foucher. 2014. Microstructure and Biogeochemistry of the Organically Preserved Ediacaran Metazoan Sabellidites. Journal of Paleontology. 88(2): 224-239.
Brian Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on December 20, 2018.












