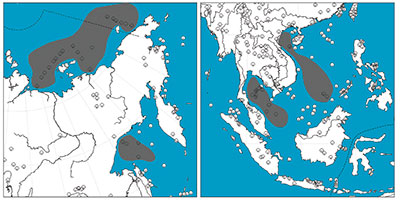
 Studies of stratigraphic data across multiple continents have revealed strong evidence of a global flood that extends to near the top of the Neogene-Quaternary (N-Q) boundary.1-4 Now the continent of Asia is divulging its rock record secrets, affirming the extent of Flood sediments. The ICR Column Team has found vast Cenozoic coal beds spread across the offshore margins of large parts of Asia (Figure 1). Some of these coals are mixed within sedimentary units that are over a mile thick.5 But just how did these coal beds get deposited so many miles offshore and across such broad regions?
Studies of stratigraphic data across multiple continents have revealed strong evidence of a global flood that extends to near the top of the Neogene-Quaternary (N-Q) boundary.1-4 Now the continent of Asia is divulging its rock record secrets, affirming the extent of Flood sediments. The ICR Column Team has found vast Cenozoic coal beds spread across the offshore margins of large parts of Asia (Figure 1). Some of these coals are mixed within sedimentary units that are over a mile thick.5 But just how did these coal beds get deposited so many miles offshore and across such broad regions?
Uniformitarian scientists claim coal originated from plants growing in place. They interpret offshore coals as the remnants of vast swamps that must have existed where the coal is located today. In other words, they think coal needs to accumulate on exposed land. But this coal extends too far offshore and is sometimes buried over a mile deep. Where was the former land surface on which these coal swamps supposedly grew?
In 2020, we reported the discovery of deep-water coals in the North Luconia region of the South China Sea, about 175 miles off of Borneo.5 These coals were found in a mile-thick section of Oligocene (middle Cenozoic) strata, two miles below sea level and in 3,000 feet of water.
There’s little evidence there was a necessary sea level drop of thousands of feet in the mid-Cenozoic to expose these continental margins. So, if these coal beds couldn’t grow in place, just how were these vast deposits spread across the offshore margins of Asia? Local catastrophes cannot explain the deep ocean locations and broad extent. The answer has to be long-distance transport on a massive scale.
ICR’s scientists have established that the Flood’s water peaked at about the K-Pg boundary (Cretaceous-Paleogene), with the bulk of the overlying Cenozoic (Neogene and Paleogene) deposited during the receding phase of the Flood, confirming the N-Q boundary as the approximate end of the Flood’s sedimentary record.6-8
Previously, we determined that the receding floodwaters produced features like the Whopper Sand in the deep Gulf of Mexico. This 1,000-foot-plus-thick Lower Cenozoic sand body is found about 200 miles offshore and is best explained by a tremendous erosional surge as the floodwaters first began to drain off the continents.2
It’s most likely that the Cenozoic coal beds flanking Asia were also produced by the Flood’s runoff processes. Vast forests on the pre-Flood uplands would have undoubtedly been ripped from the land as the floodwaters crested on Day 150. These huge mats of vegetation would have been transported off the continents like the Whopper Sand was and buried in the ocean as the Flood receded.5 Today, the buried vegetation is found in the form of subsurface coal beds off the southeast Asian coast, the South China Sea, the Okhotsk Sea, and spread across the East Siberian Shelf, Laptev Shelf, and Russian Chukchi Shelf (Figure 1).9-15
The global Flood truly left its mark carved in stone.1 Secular stories of exposed coal-rich swamps are inadequate to explain these extensive offshore deposits. Instead, these coals serve as a testimony to both the power and the truth of the Genesis Flood.
References
- Clarey, T. 2020. Carved in Stone: Geological Evidence of the Worldwide Flood. Dallas, TX: Institute for Creation Research.
- Clarey, T. A Whopper Mystery for Nearly 20 Years. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org April 22, 2020, accessed March 25, 2021.
- Clarey, T. and J. J. S. Johnson. 2019. Deep-Sea Dinosaur Fossil Buries Evolution. Acts & Facts. 48 (8): 10-13.
- Clarey, T. 2019. European Stratigraphy Supports a Global Flood. Acts & Facts. 48 (12): 10-12.
- Clarey, T. 2020. Deep Water Coals Discovery Supports Flood. Acts & Facts. 49 (8): 9.
- Clarey, T. 2020. Compelling Evidence for an Upper Cenozoic Flood Boundary. Acts & Facts. 49 (5): 9.
- Tomkins, J. P. and T. Clarey. 2020. Paleontology Confirms a Late Cenozoic N-Q Flood Boundary. Acts & Facts. 49 (11): 10-13.
- Clarey, Carved in Stone, 312-353.
- Nguyen, H. H. 2018. The Cenozoic evolution of the South Vietnam margin of the South China Sea and the origin of coastal placer deposits. Ph.D. dissertation. Birkbeck, University of London.
- Polachan, S. et al. 1991. Development of Cenozoic basins in Thailand. Marine and Petroleum Geology. 8 (1): 84-97.
- Fujiwara, M. 2012. Significance of the Middle Miocene Unconformity on petroleum geology in the Pattani Trough, Gulf of Thailand. Ph.D. dissertation. Chiba University, Japan.
- Hoang, B. H. et al. 2020. Paleogene structural development of the northern Song Hong Basin and adjacent areas: Implications for the role of extrusion tectonics in basin formation in the Gulf of Tonkin. Tectonophysics. 789: 228522.
- Gnibidenko, H. S. and I. I. Khvedchuk. 1982. The tectonics of the Okhotsk Sea. Marine Geology. 50 (3): 155-198.
- Drachev, S. S. et al. Geology and petroleum systems of the Russian Arctic sedimentary basins. AAPG 3P Arctic Conference and Exhibition. The Polar Petroleum Potential, hosted by Russian Geological Society, September 30–October 2, 2009, All-Russian Exhibition Center, Moscow, Russia.
- Lunt, P. 2020. A reappraisal of the Cenozoic stratigraphy of the Malay and West Natuna Basins. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences. 5 (1): 100044.
* Dr. Clarey is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in geology from Western Michigan University.










