Ever had a blood test? Along with a value measured, there are also the normal max/min limits for that value. This implies that the body normally controls that quantity between those limits. How does it do that?
It measures the value and produces more or less of that quantity based on the value measured. This is called a control loop. There are hundreds of thousands, perhaps millions, of control loops in the human body.
To understand the components of a control loop, let us look at a familiar example: controlling the temperature in your home. A thermostat measures the room temperature. The logic is to turn the power to the heater on if the room temperature is below a set temperature, T1. When the temperature rises above a second set temperature, T2, the thermostat turns the power off.1 This control loop is shown in Figure 1. It is called a loop because the heater output, the heat, is looped back through the room to the thermostat (called feedback) to provide control.
In summer, when the ambient temperature is high, the heater remains off. Note that all the components of the heating system are still there—the thermostat, the heater, and the power to run it. The heating system does not “devolve” in summer, it is just quiescent. In winter, when temperatures are low again, the heat comes back on. The heating system did not re-evolve. It was there all the time, just latent!
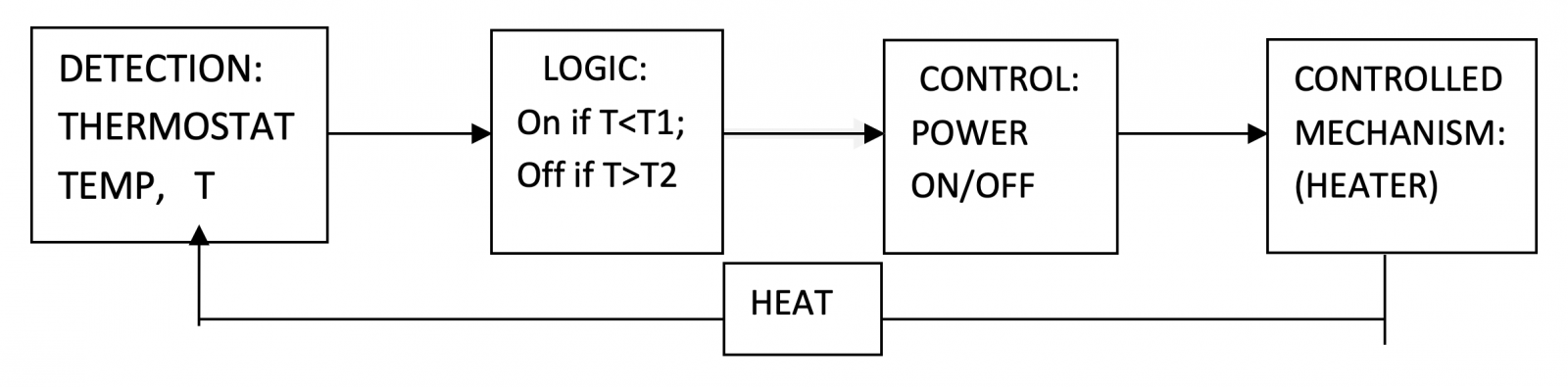
The above system is an example of continuous environmental tracking (CET) or monitoring. The thermostat is continuously monitoring the temperature, i.e. the environment, and is ready to respond when needed.
We find similar systems in the human body. Some examples are sweating when hot and shivering when cold. These reactions occur only when needed, as in the heating control loop above, and are otherwise latent.
Biological control loops function by turning hormones and/or genes on and off, like the power example above. Similar to the thermostat in summer, some can be latent for extended periods. For example, blood doesn’t clot (fortunately) until we have a cut. Then, many mechanisms turn on to stop the bleeding. They turn off when the bleeding is stopped. In this example, there are loops within loops (called nested loops) that can provide coarse and fine control. The control loops are always there, operating when needed, similar to the heater loop above.
Control loops governed by genes may be off for long periods of time, even for a lifetime, by epigenetics, as in adaptation. The controlling genes remain (every cell has the full genome) but just aren’t active or expressed (like turning off the power). A chemical binds to specified DNA regions turning genes off or on, disabling the control loop. On a micro-scale, nerve cells and muscle cells have the same DNA, but because different genes are turned on/off, they have entirely different attributes and functions. The same genome is still there, just adapted. On a macro-scale, epigenetic changes can be inherited and help people adapt to their environments.
In conclusion, functional changes are easily explained by biological control loops continuously monitoring their environment. They may be active, latent (ready when needed), or turned off. They explain biologic functioning and adaption. Evolution/devolution doesn’t make sense.
Notes
1. When a control loop has only two states—power fully on or off—it’s called a bang-bang control loop. This differs from the more common proportional control loop, or servo loop.
2. In mechanical thermostats, the detection and logic are combined.
*Dr. Siebert earned his Ph.D. in equations of quantum mechanics from the Polytechnic Institute of New York University. He is a freelance contributor to ICR’s Creation Science Update, has worked 40 years in electro-optics, and held numerous patents.




