As mere fragments, most fossils reveal only small hints of ancient life forms, like a single segment from a crinoid stem, or a lone hadrosaur tooth. But a fossilized fern's stem recently discovered in Sweden shows its every detail, sending some clear messages about its origin.
Publishing in the journal Science, three authors from Sweden described the spectacular sub-cellular preservation of a royal fern in Jurassic rock.1 Mineral-rich water infiltrated its tissues faster than they could even begin to disintegrate.
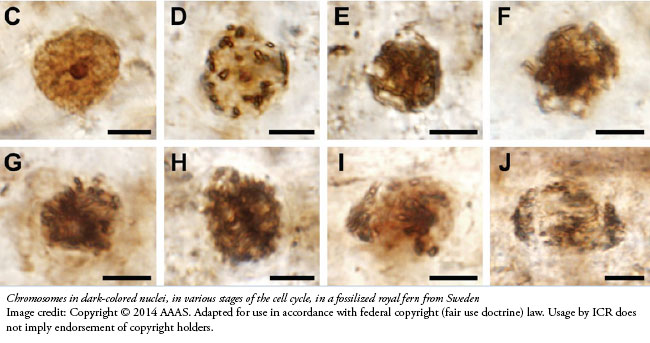
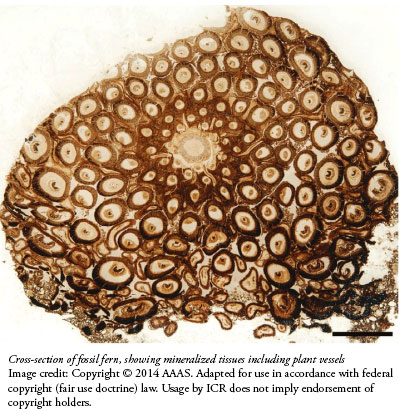 The team cut the fossil into thin slices and placed them under a microscope to see "membrane-bound cytoplasm, cytosol granules, [and] possible amyloplasts" within the fern cells. Equally rare were the cells' nuclei "with conspicuous nucleoli," tiny structures inside each nucleus.
The team cut the fossil into thin slices and placed them under a microscope to see "membrane-bound cytoplasm, cytosol granules, [and] possible amyloplasts" within the fern cells. Equally rare were the cells' nuclei "with conspicuous nucleoli," tiny structures inside each nucleus.
They even found chromosomes frozen in various stages of cell division, including prophase, telophase, metaphase and possibly anaphase.
The researchers compared the fossil chromosomes to those of living royal ferns and found no differences. They wrote, "Here, we present direct paleontological evidence for long-term genomic stasis in this family in the form of a calcified osmundaceous [royal fern] rhizome [tiny root structure] from the Lower Jurassic of Sweden with pristinely preserved cellular contents, including nuclei and chromosomes."1
After 180 million supposed years to work its magic, how could the neo-Darwinian engine of natural selection of beneficial mutations not have made some changes to this fern? Yet the fern remains the same.
During this same proposed timespan, some furry little mammal supposedly evolved all the way to people—a fantastic story involving wholesale reorganizations of dozens of fundamentally distinct body forms—while not one chromosome of the royal fern changed at all.
The study authors wrote that this fossil comparison "represents a notable example of evolutionary stasis among plants."1 Instead of merely "notable," perhaps they should have said, "impossible."
Plus, isn't "evolutionary stasis" an oxymoron? Evolution is supposed to mean "constant change," and "stasis" means "no change." Something unscientific appears to be going on within a scientist who interprets even a total lack of evolution in an evolutionary way.
The similarity between a living royal fern and its fossil counterpart plainly presents a problem for millions-of-years. Why do these ferns look so similar? Because their ancestors were ferns that God created only thousands of years ago, according to His own eyewitness testimony.2
References
- Bomfleur, B., S. McLaughlin, and V. Vajda. 2014. Fossilized Nuclei and Chromosomes Reveal 180 Million Years of Genomic Stasis in Royal Ferns. Science. 343 (6177): 1376-1377.
- Genesis 1:12.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on April 16, 2014.