In late June, Forbes magazine published an article by environmentalist and climate activist Michael Shellenberger in which he apologized for thirty years of climate alarmism promoted by the environmental movement.
Shellenberger thinks climate change is happening, but he does not think it is the catastrophe that it is often made out to be. In fact, he doesn’t even think it is the most serious of environmental problems. The original article is apparently no longer available on the Forbes.com website, but an archived PDF of his article may be read elsewhere.1 The article is a brief summary of an argument he makes in greater detail in his new book Apocalypse Never: Why Environmental Alarmism Hurts Us All.2
Shellenberger notes that, despite his denunciation of climate alarmism, he is not a “right-wing anti-environmentalist.”1 He has a long record of environmental activism, starting at the age of 16 when he fundraised for the Rainforest Action Network. He helped save the last unprotected redwood trees in California and has been a strong past supporter of renewable energy sources.1 He is a recipient of Time magazine’s “Hero of the Environment” award.3 He has provided expert testimony to the United States Congress and has been asked to serve as an expert reviewer for the next Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report.1
Shellenberger claims that much of the “conventional wisdom” regarding climate change is simply wrong. He also says that in the past he refrained from speaking out against climate alarmism for two reasons. First, he was embarrassed, as he himself had made some of those same alarmist claims. Second, he was afraid to do so, for fear of “losing friends and funding.” In fact, he says that on the few previous occasions on which he did speak out against misrepresentation, he suffered for it.1
This should serve as a wake-up call for those who have naively idolized scientists as objective seekers of truth motivated by nothing more than a love for truth and logic. As long-time followers of the creation-evolution controversy well know, scientists—being human—are often motivated by other factors. One simply cannot naively assume that scientists are always objective! In fact, professionals in other areas are often afraid to contradict the “consensus” view, as demonstrated by the recent dramatic resignation letter of New York Times columnist and editor Bari Weiss.4,5
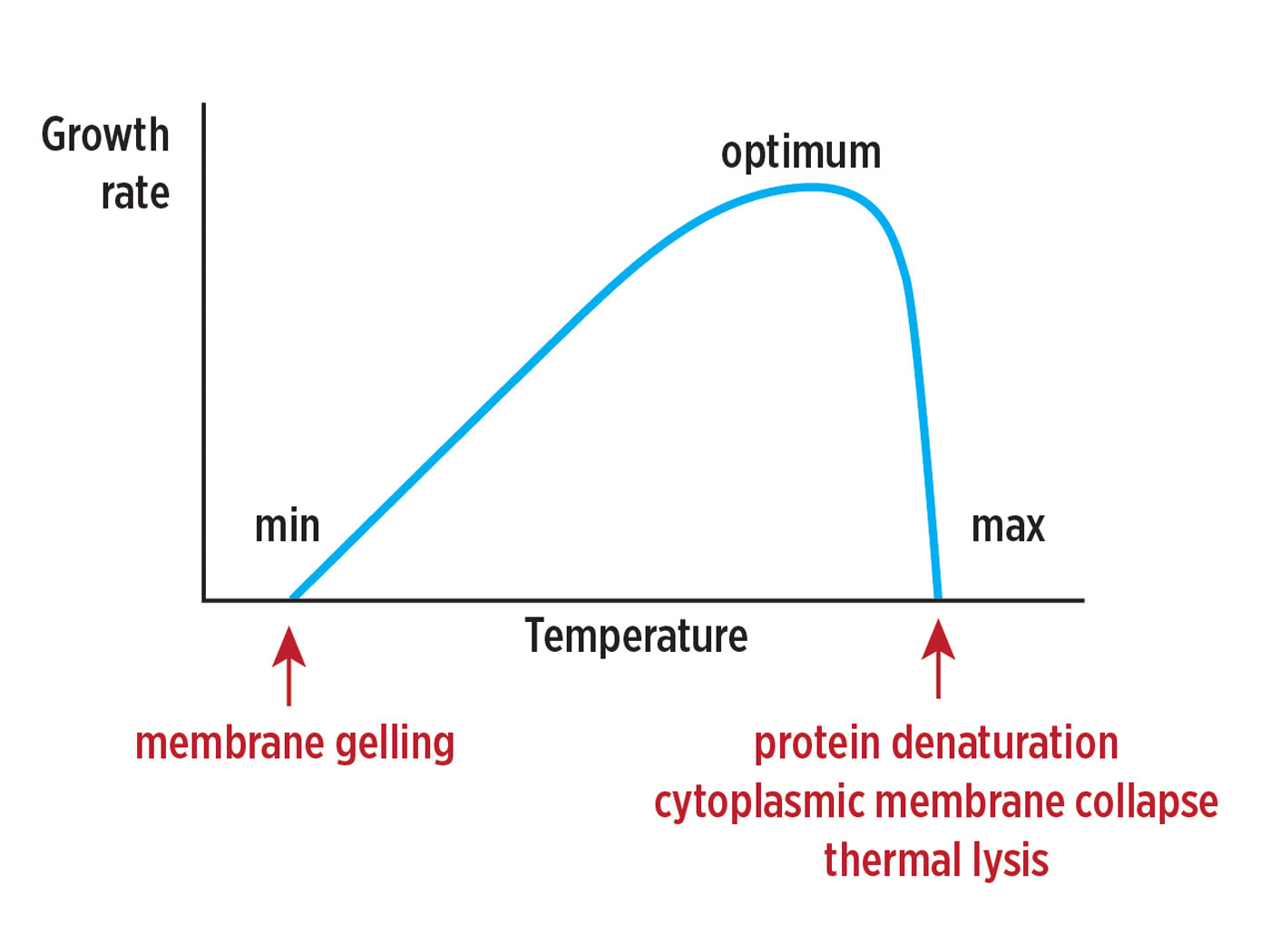
Indeed, evolutionary and old-Earth beliefs, particularly acceptance of the secular Milankovitch (or astronomical) ice age theory, is a major contributor to climate alarmism,6 despite the fact that original ICR research has revealed that evidence for the theory is incredibly shaky, even if one accepts the typical old-Earth age assignments.7
This should be a reminder that only God and His Word should be trusted without reservation. Because we humans are sinful and fallible, we should “test” what others (including scientists) say—including what they say about the subject of origins.
References
1. Shellenberger, M. On Behalf of Environmentalists, I Apologize for the Climate Scare. Forbes. Posted on forbes.com June 28, 2020, accessed at wattsupwiththat.com July 15, 2020.
2. Shellenberger, M. 2020. Apocalypse Never: Why Environmental Alarmism Hurts Us All. New York: HarperCollins Publishers.
3. Shellenberger, M. Contributor Description. Forbes. Posted on forbes.com, accessed July 15, 2020.
4. Weiss, B. Resignation Letter. Bari Weiss website. Posted on bariweiss.com, accessed July 15, 2020.
5. Flood, B. Bari Weiss quits New York Times after bullying by colleagues over views: ‘They have called me a Nazi and a racist.’ Fox News. Posted on foxnews.com July 14, 2020, accessed July 15, 2020.
6. Hebert, J. 2019. Climate Alarmism and the Age of the Earth. Acts & Facts 48(4).
7. Hebert, J. Physics Today Article Ignores Monster Milankovitch Problem. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org May 24, 2020, accessed July 15, 2020.
*Dr. Jake Hebert is Research Associate at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his Ph.D. in physics from the University of Texas at Dallas.
Environmentalist Apologizes for Climate Change Alarmism
The Latest
Confirmed New Record for Most Distant Galaxy
A galaxy with the designation MoM-z14 has recently been confirmed as the most distant galaxy ever detected.1,2 By Big Bang reckoning, we...
Insect Eyes Reflect Creation
Research into insect eyes continues to reveal amazing structure and function. For example, although fruit flies’ eyes are attached firmly to their...
February 2026 ICR Wallpaper
"Be strong and of good courage, do not fear nor be afraid of them; for the LORD you God, He is the One who goes with you. He will not leave you...
Microgravity's Effect on Bacteriophages Is Not Evolution
The word evolution is often used imprecisely, leading the public to believe that any biological change is evolution, and, therefore, it’s a fact.1...
Engineered for Extremes: The Hidden Precision of a Salt Lake...
Water that is nearly five times saltier than the ocean is deadly to most animals. But in Utah’s Great Salt Lake, scientists have found a tiny...
CREATION PODCAST
Giant Sequoias: Too Complex to Be Accidental | The Creation Podcast:...
What living thing grows taller than a 25-story building, survives raging wildfires, and actually depends on those fires to reproduce? Giant sequoias...
Bound by Design: How a Universal Temperature Law Reveals Life’s...
What if every living creature—from coral reefs and cold-water fish to mountain flowers and desert reptiles—followed the same hidden temperature...
The Flood Explains 18,000 Dinosaur Tracks in Bolivia
A new discovery of 18,000 individual dinosaur tracks in the Bolivian El Molino Formation contains the highest number of theropod dinosaur tracks in...
Prolonged 40-Year Growth in T. Rex: Evidence for Pre-Flood Longevity?
An open access 2026 PeerJ research paper claims that T. rex took 40 years to reach its full adult body size, in contrast to a much shorter previous...
Recent Discovery of a Strange Microbe Gives No Clues to Evolution
Research into God’s living creation is dynamic and always surprising. This is true whether one peers into the deepest reaches of space or dives...