U.S. companies have ramped up oil and gas production over the last four years, using cutting-edge techniques to extract oil from shale. Lejly Alic, an analyst with the International Energy Agency, recently told the New York Times, "We keep raising our forecasts, and we keep underestimating production."1 Where did all this shale oil come from?
The new extraction technology, called "fracking," uses pressurized water-chemical-sand mixtures to fracture shale layers, releasing their trapped oil and gas reserves.
Shale is a rock type defined by its high clay content and thin layers that flake apart. Layers without much organic content appear grey, tan, or a number of other colors depending on their mineral makeup, while shales bearing organic compounds like oil look blackish. The organics were once living creatures, perhaps marine algae like those that supplied the world's largest oil reserves. At some point, they became intermixed in clay-rich mud.
Today, these rock beds hold so much organic material, converted into oil and gas, that the U.S. may soon exceed Saudi Arabia's production volume.2
It would be easier to explain the origin of shale oil if it were only found in a few, limited spots. But its reach is extensive with shale making up at least 50 percent of all sedimentary rocks. A government map of shale-rich U.S. areas shows them stretching from California's San Joaquin Basin to the Appalachian Basin as far as New York.3
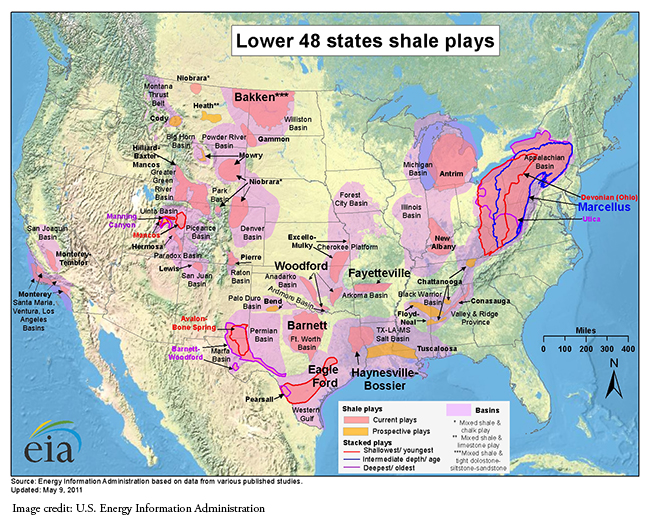
Because shale deposits are not currently forming anywhere, reconstructing their origin requires a bit of forensic thinking.
Normal, slow-and-gradual processes don't fully satisfy as an explanation. If a die-off in algae occurred in some ancient, mid-continent mini-ocean, then wouldn't Earth's voracious ecosystems rapidly recycle the organic debris, as has occurred in today's oceans? It is difficult to imagine how the organics were trapped in mud before they decayed, especially considering the speed of bacterial action.4
Some abnormally rapid and energetic processes must have covered those organics with huge amounts of mud, quickly preserving them within thick stacks of sediments before they could rot. Ever since, the oil has been leaking out, rising through more dense rock and water.
If rapid cataclysmic mud flows, not slow and gradual processes, better explain these shale deposits, then could catastrophic flooding have occurred millions of years ago, burying vast plains of marine algae that turned to oil as they decomposed among hardening shale layers?
This scenario still does not satisfy since it does not explain how oil could persist underground for so long. Oil constantly migrates through fissures, fractures and breaks, but it has yet to be either completely eaten by bacteria or oxidized into smaller, simpler chemicals.
Shale is defined by breaks along its bedding planes. Fracking merely accelerates the retrieval of oils that would ordinarily escape much more slowly, but not slowly enough to still be down there after millions of years.5
It seems that the best explanation for today's huge shale reserves requires a watery catastrophe almost too calamitous to imagine. The Noahic Flood fits the bill. And perhaps the best way to account for oil's persistence—in unforeseen volumes—is to think of these deposits in ages of thousands, not millions of years.
References
- Norris, F. U.S. Oil Production Keeps Rising Beyond the Forecasts. New York Times. Posted on nytimes.com January 24, 2014, accessed March 12, 2014.
- Usborne, D. Fracking is turning the US into a bigger oil producer than Saudi Arabia. The Independent. Posted on independent.co.uk March 11, 2014, accessed March 12, 2014.
- Lower 48 states shale plays. U.S. Energy Information Administration map. Posted on www.eia.gov May 9, 2011, accessed March 12, 2014.
- Thomas, B. Oil-eating Bacteria Are Cleaning Up Gulf. Creation Science Update. Posted on icr.org August 27, 2010, accessed March 12, 2014.
- Clarey, T. 2013. Oil, Fracking, and a Recent Global Flood. Acts & Facts. 42 (10): 14-15.
*Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on April 2, 2014.




