The alleged great age of earth's geologic strata has been characterized by evolutionists as representing millions of years of accumulation of sediments under water. Modern observers are generally willing to recognize evidence of rapid deposition of the strata by catastrophic processes, but insist that great ages passed between depositional episodes. During these long ages, erosion may have occurred, but they say the whole package required great ages.
Creationists, on the other hand, consider that the bulk of earth's sedimentary rock accumulated rapidly beneath the waters of the great Flood of Noah's day. One layer followed another in swift succession, sometimes interrupted by brief periods of quiescence, uplift, and erosion. Some time may have passed between depositional events, but these periods were not long, and the bulk of the sedimentary rock record may represent hardly more than one year.
Since both young and (most) old earth advocates agree that the strata themselves represent short periods of time, an estimate of the length of the non-depositional and erosional periods will give us the approximate time required for the whole. This draws our attention to the upper surface of each layer. Is there evidence that it lay exposed for great ages, or was it quickly covered by the next layer?
Looking like sand on a seashore, many layers exhibit "ripple marks." Yet ripple marks in loose sand last only until the next tide. Even in hard rock they erode within a few years. Their nearly ubiquitous presence on sandstone surfaces argues for quick burial perhaps by the next wave, protecting them until they hardened.
A similar line of reasoning notes that animal burrows and plant roots, etc., can be found on every modern soil surface, on land or in water. Why are they rare to non-existent in the geologic record? Sometimes a fossil tree or animal body will intersect more than one layer. Called "polystrate" fossils, they demand a short time between layers.
An erosional surface in the rocks is called an unconformity, and some amount of time is necessitated between two unconformable layers. But unconformities are not worldwide. When traced laterally they often grade into conformity, implying continual (rapid) deposition, of the sequence. On a larger scale, entire geologic periods, like the Cambrian or Ordovician are present, implying a short duration. Sometimes they grade conformable into the next period.
Somewhere in the world the middle Cambrian grades conformably into the upper Cambrian, which somewhere grades into lower Ordovician then middle Ordovician and so on. From the Cambrian upwards the geologic strata are a record of continuous, catastrophic, rapid deposition under flood waters. This is what we would expect based on the Biblical account of the great Flood.
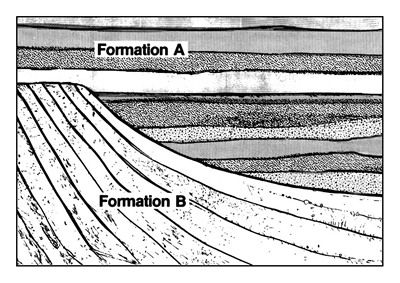
Limited Extent of Unconformities














