In January 95 of this column, I reviewed the grand opening of the new evolution exhibit, "DNA to Dinosaurs," at the Chicago Field Museum of Natural History. I pointed out many inaccuracies in the exhibits, even bad evolution. Yet the brainwashing effect was tragically effective.
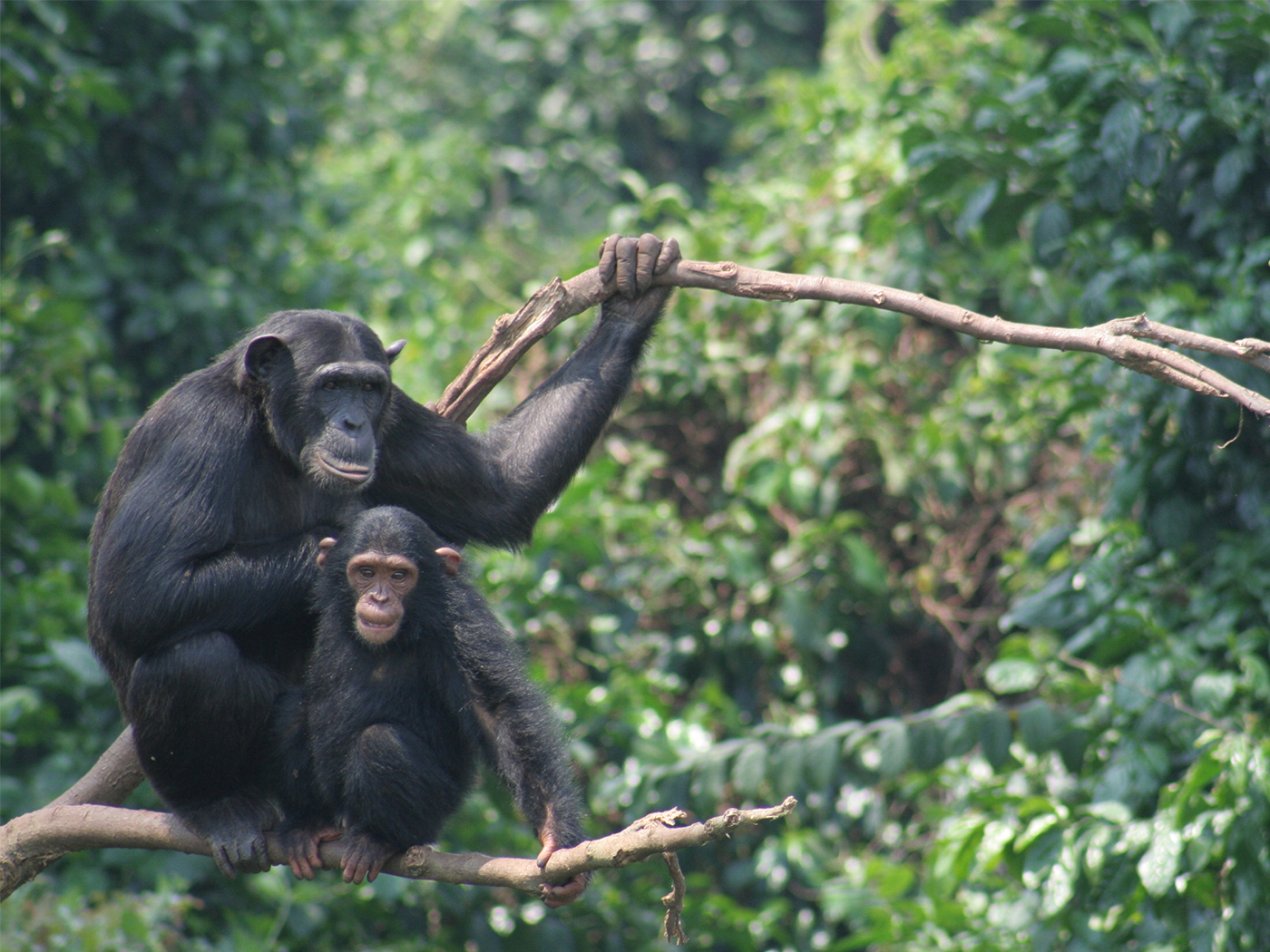
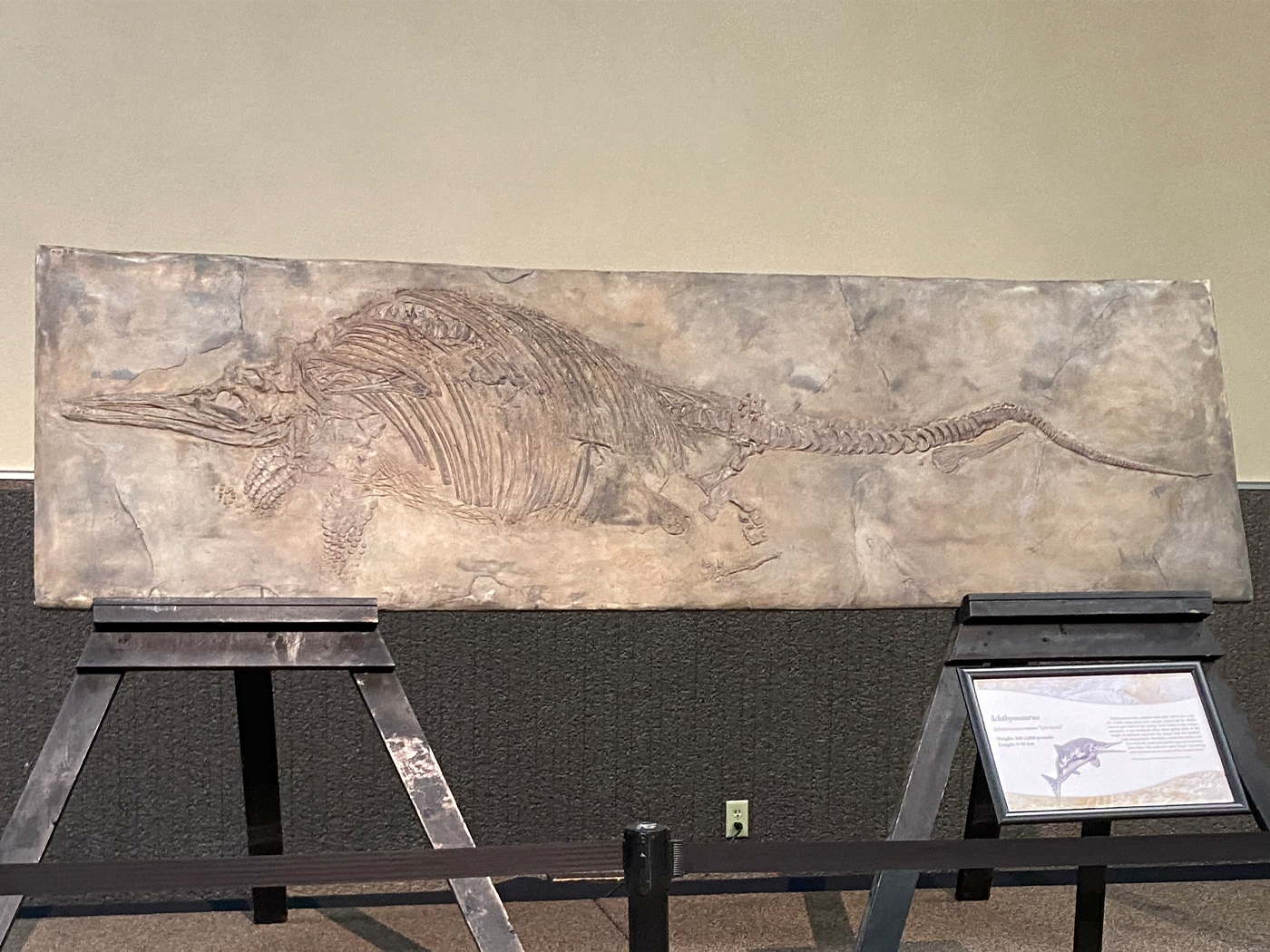
The museum pulled a slick trick when it discussed the supposed evolution of amphibians from fish. This transition was mentioned in three displays, and heralded as a triumph of evolution theory. Only one trouble—three distinctly different fish ancestors were mentioned. Each one was presented authoritatively, with no mention of the other options or the obvious scientific controversy surrounding them.
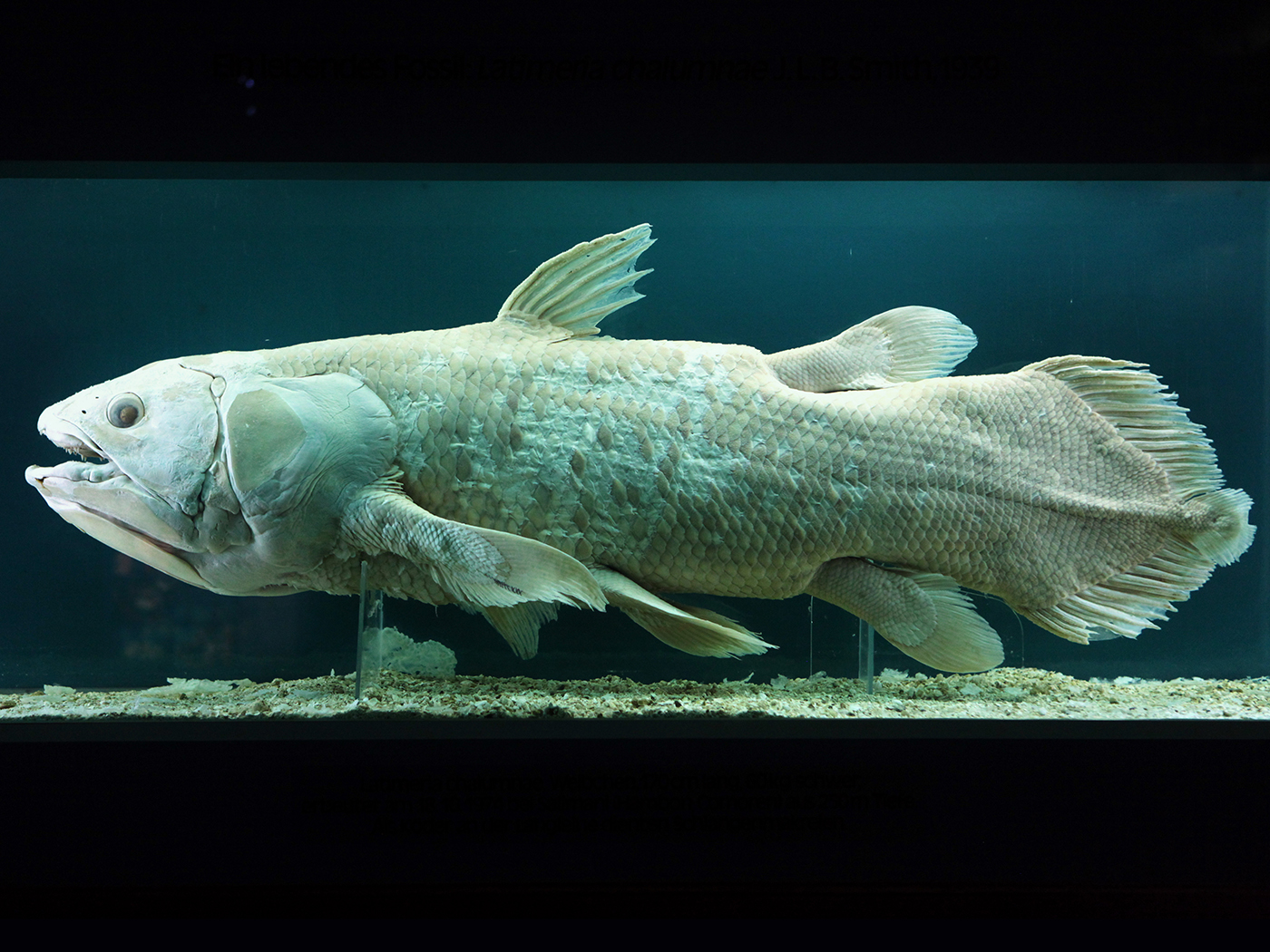
One was the famous "living fossil" known as the coelacanth (order, Coelacanthiformes). This type of fish, previously known only from fossils, had certain structures in its fins, and for years was thought to have been the ancestor of the amphibians and later all other land animals. But in 1938 a living specimen was found off the coast of Africa and others have been found since. Evolutionists' joy turned to consternation when it was seen that soft anatomy was not at all like an amphibian, nor did it live in shallow areas about to crawl out on land. It lives in the deep ocean and uses its stronger fins to navigate in unusual ways, but never to "walk" along the bottom. Today few evolutionists still hold to the coelacanth as an ancestor to land animals, but there it was in the museum.
A majority of today's evolutionists hold to the idea that a similar type of fish (order, Rhipidistia), led to amphibians. Again, this fossil fish had structures in its fins, and a loose comparison could be made with the femur and humerous (arm and leg bones in land animals), but nothing to compare to hands and feet. Furthermore, as is also the case in the coelacanth, the hard parts of the fins are loosely embedded in muscle, not at all attached to the vertebra as required to support the weight of the body. In the amphibian thought to be the oldest, both the pelvis and shoulder are large and strong. Where did they come from?
A third suggestion was the lungfish (order, Dipnoi), which is known to gulp air in addition to breathing through its gills. This remarkable fish can survive buried in mud during periods of drought, undergoing an extremely dominant state, but his "gulping" has nothing to do with it. Despite the fact that many high school students are taught that lungfish evolved into land creatures and the museum reinforced this idea, few evolutionists consider any form of lungfish to have been the forerunner of amphibians, mainly because of skeletal differences, for the lungfish has no hint of legs. Only museum visitors are still mistaken.
Actually the skeletal differences are only one of the many problems encountered in trying to link fish and amphibian. The internal organs are quite different also. Major changes would have had to occur in just the right order to accomplish the transition. For instance, while the pelvic girdle is forming (by mutation), and the gills are mutating into true lungs and the ears and eyes must mutate to work in the dry air. How could any possible ancestor accomplish these and other simultaneous changes?
The problem would be solved if we could find fossils of transitional forms, but alas, no "fishibian" has ever been found. Every fish, living or fossil, even those with unusual characteristics, is fully fish, and every amphibian, living or fossil, is fully amphibian.
To make matters even worse, a fossil amphibian has recently been found which "dates" even older than those "primitive" amphibians thought to be most fish-like. Yet it is 100% amphibian, just like it ought to be if (or should I say since) creation is true.
* Dr. Morris is President of ICR.