A recent paper published in Proceedings of the Royal Society B may have inadvertently confirmed what the Bible revealed to us all along: Kinds only reproduce after their kinds.1
Kinds only reproduce after their kinds. ![]()
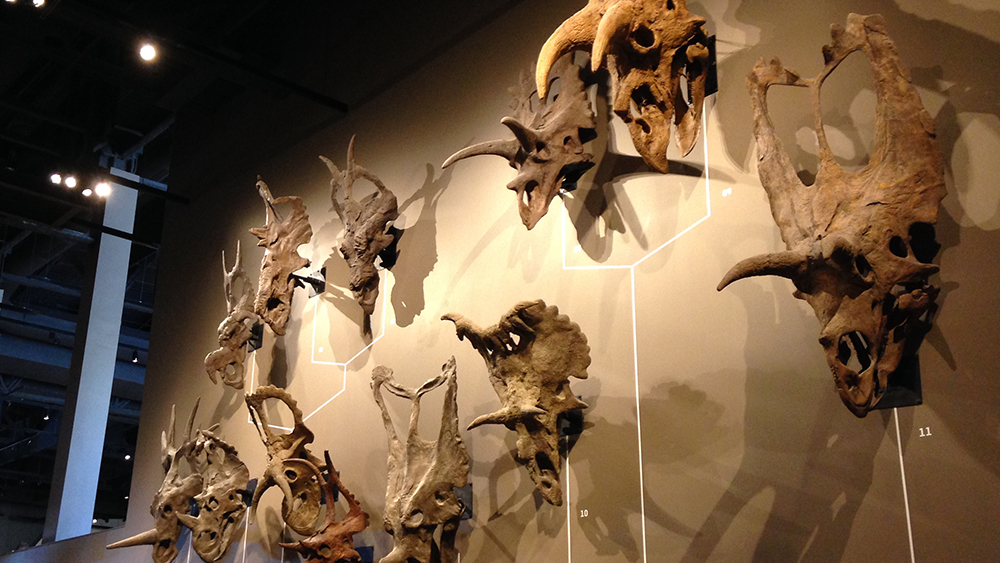
Ceratopsian dinosaurs are the horned varieties that include Triceratops and Styracosaurus. These dinosaurs share a common body structure and seem to only differ in their ornamentation, which includes their frill shape and of course horn varieties.
This new study by Andrew Knapp of Queen Mary University, London, and his colleagues from the Raymond M. Alf Musuem of Paleontology in Claremont, California, and the Natural History Museum of Utah in Salt Lake City, attempted to determine why ceratopsian dinosaurs have so many different varieties of horns and frills.1
It’s well known that the number and sizes of horns and frill ornamentation on the Ceratopsian dinosaurs vary considerably. These ornamentation differences may have helped establish social status or could have been due to differences in the sexes. Some paleontologists have noted that hatchling ceratopsians all looked very much the same.2 It wasn’t until they matured that the horns and frills took on distinctive character, leading to the notion that these differences were possibly for recognition within family units.
A news post at Scientific American noted,
It’s something of a running joke that horned dinosaurs are just different heads on the same chassis. The new study [by Knapp et al.] adds actual data to this impression, meaning that either there was a greater evolutionary push to evolve vastly different horn arrangements or that bodies of these dinosaurs were under what’s called a “stabilizing selection,” the biomechanical traits of their bodies being more resistant to change. The reason for this pattern remains unknown.3
Knapp and his co-authors suggest several possible explanations for the rapid diversity of ceratopsian horns and frill ornaments, but were unable to reach any statistically valid conclusions.1 They even dismissed the concept of sexual dimorphism—differences between the sexes—to explain horn and ornament differences.
Most studies of sexually selected ornaments and weapons in extant taxa focus on sexually dimorphic examples, and there is no clear evidence of sexual dimorphism in Ceratopsia or any other dinosaur clade. Except in extreme examples, large sample sizes are needed to distinguish sexes based on morphology alone.1
These differences can be simply explained as variations within the same species or kind, just like dogs have vastly different sized and shaped breeds today. ![]()
Creation scientists believe that horn and frill differences in many of the ceratopsian dinosaurs do not necessarily establish separate species, or even different sexes. Rather, these differences can be simply explained as variations within the same species or kind, just like dogs have vastly different sized and shaped breeds today. Evolutionary scientists are prone to name any noticeable difference as a new species, artificially inflating the total number of dinosaurs.2 Could it be that God simply loves diversity in His created kinds?
References
- Knapp, A. et al. 2018. Patterns of divergence in the morphology of ceratopsian dinosaurs: sympatry is not a driver of ornament evolution. Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 285: 21080312. Genesis 1: 21-25.
- Clarey, T. 2015. Dinosaurs: Marvels of God's Design. Green Forest, AR: Master Books. Available at ICR.org/store.
- Switek, B. The latest in horned dinosaur fashion. Scientific American. Posted on scientificamerican.com April 11, 2018, accessed May 9, 2018.
Stage image: Ceratopsian skulls at the Natural History Museum of Utah.
*Dr. Timothy Clarey is Research Associate at ICR. He earned a Ph.D. in geology from Western Michigan University