Whether considering squishable apple tissue or resilient tree trunks, researchers say that plants "build" their parts using only four ingredients. Precise measurements of plant tissue strengths show that they vary across three orders of magnitude. How do plants so effectively use the same four building blocks to manufacture materials with such widely varying strengths?
MIT engineering professor Lorna Gibson found five features that plants "control and coordinate" when building tissues of various strengths. According to MIT news, "It turns out the large range in stiffness and strength stems from an intricate combination of plant microstructures."1
She published her review in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, where she wrote, "Apples and potatoes are examples of a simple tissue: parenchyma with thin-walled, polyhedral cells resembling an engineering closed-cell foam." Researchers deem that hardwoods contain complex tissue because in addition to parenchyma cells they have vessels and fibers. "The fibre cells provide structural support and have a honeycomb-like structure" similar to that used in hexagonal building supports.2
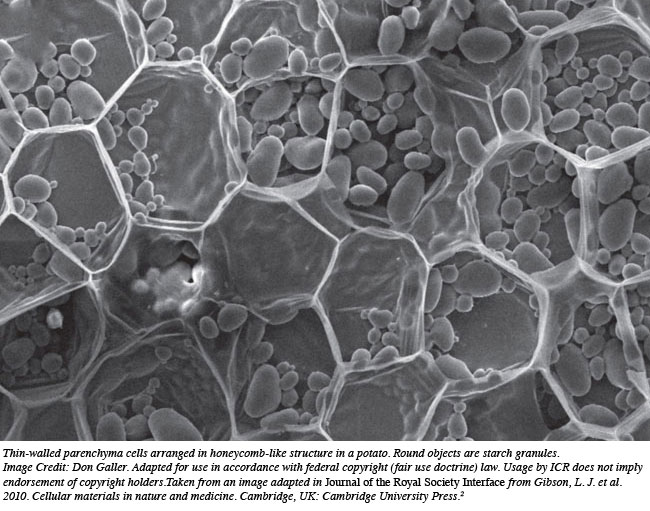
But whether it contains fiber cells or parenchyma tissue, plants all build their cell walls using cellulose, lignin, hemicellulose, and pectin. Plants expertly arrange these ingredients to form tissues of widely ranging strengths. Gibson wrote, "These large ranges arise from the composition of the cell wall, the number of layers in the cell wall and the volume fraction and arrangement of cellulose fibres in those layers, as well as the cellular structure of the plant tissue."2
"Gibson sees plant mechanics as a valuable resource for engineers concerned with designing new materials. But researchers have been unable to fabricate cellular composite materials with the level of control that plants have perfected," according to MIT news.1 What or who deserves the credit for the masterful way that lowly plants organize their own building materials?
Gibson said that "plants have developed" their own microstructures. Cornell plant biologist Karl Nicklas told MIT that because plants evolved, "We can learn things from nature and apply it to construct better panel boards, styrofoams and photovoltaics that will help society."1
But what reason or evidence even hints that plants or nature can engineer anything, let alone construction techniques and material management that surpasses man-made technology? Plants don't have brains or hands like human engineers possess.3 Those who deem plants to be expert engineers would not entrust a plant to produce even something so simple as a fork. When it comes to origins science, brilliant engineering professors are barking up the wrong tree.
References
- Chu, J. Plants exhibit a wide range of mechanical properties, engineers find. MIT news. Posted on mit.edu August 14, 1012.
- Gibson, L.J. The hierarchical structure and mechanics of plant materials. Journal of the Royal Society Interface. Published online before print, August 8, 2012.
- According to Scripture, God did not necessarily use brains or hands to create either. However, He has something far more effective: audible commands spoken from beyond this universe. See Psalm 33.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on August 22, 2012.











