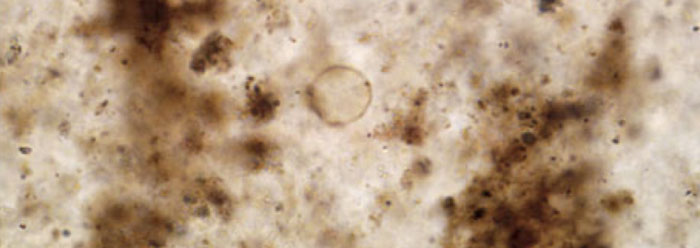
Rock researchers highly regard Ontario's Gunflint chert for its fresh-looking microfossils. Long ago, the chert's microcrystalline quartz grains embedded microscopic single-celled creatures, including algae. A research team used new techniques to analyze the chemicals inside these fossil cells. They found protein remnants where they should no longer exist—given these rocks' vast age assignment.
The team of French scientists partnered with UCLA ion-microprobe specialist Kevin McKeegan to publish in the online journal Nature Communications.1 Their investigation of tiny algae cells revealed remnants of original biochemistry despite their evolutionary age assignment of 1.88 billion years.
Microprobe analyses gathered information from organic microfossils collected from five different outcrops of the same rock layer. The study authors wrote, "In fact, despite the 1.88-Gyr-long geological history that they experienced, Kakabeka Falls [outcrop] and Schreiber Beach [outcrop] organic microfossils exhibit C- and N-XANES spectra sharing strong similarities to those of modern cyanobacteria and modern micro-algae."1 They apparently used the word "despite" to acknowledge the disparity between the rocks' evolutionary age expectations and the presence of original biochemicals.
Many chert-rich rocks experienced temperatures high enough to bake any biochemicals. Heat can turn them into blackened, more-resistant compounds. But the Gunflint chert contains signs of a cooler formation history. This certainly helped convey these actual chemicals from the cells entombed so long ago until today.
The scientists used the same spectral analysis on modern photosynthetic bacteria and single-celled algae as the fossil versions, since both look so similar. In other words, it appears that none of the expected evolution has occurred across 1.88 billion supposed years.
The study authors wrote, "In addition, these microfossils still contain amide functional groups (absorption feature at 288.2 eV), which were likely to be involved in the proteinaceous compounds synthetized by the once living organisms."1 Biochemistry studies reveal that amide bonds have plenty of potential to perform spontaneous chemistry. What are the odds that these bonds completely missed almost 2 billion years' worth of opportunities to decay?
Proteins should have undergone chemical reactions with any number of nearby chemicals, totally obliterating the original proteins in far fewer than a million years. Three orders of magnitude separate protein's longevity based on repeatedly measured decay rates and the evolutionary age assignment for this deposit that houses algal protein remnants.
If the Gunflint chert was emplaced only thousands of years ago, then these dilemmas evaporate.2
References
- Alleon, J. et al. 2016. Molecular preservation of 1.88 Ga Gunflint organic microfossils as a function of temperature and Mineralogy. Nature Communications. 7: 11977.
- This short time scale fits the idea that most rocks were deposited during the single Flood year, not over billions of years. Different processes in the pre-Flood world may have deposited the Gunflint chert, along with Michigan's banded iron formations and other nearby stromatolite-rich layers.
Image credit: Copyright © 2016 Macmillan Publishers Limited, part of Springer Nature. All rights reserved. Partner of AGORA, HINARI, OARE, INASP, ORCID, CrossRef, COUNTER and COPE. Adapted for use in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
*Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on July 21, 2016.