Are Ediacaran "fossils" actually remains of ancient living things, or did simple natural processes generate fossil look-alikes? Correctly identifying these tracks (or traces) matters significantly to those who insist these Ediacaran rocks—which secularists believe to be over 550 million years old—came from a time when Earth's earliest animal life first appeared. Are these scientists looking at fossils made by the supposed ancestor common to all animals?
The latest research reveals enough clues to discern a clear answer. And along the way, secular scientists encountered evidence that confirms special creation.
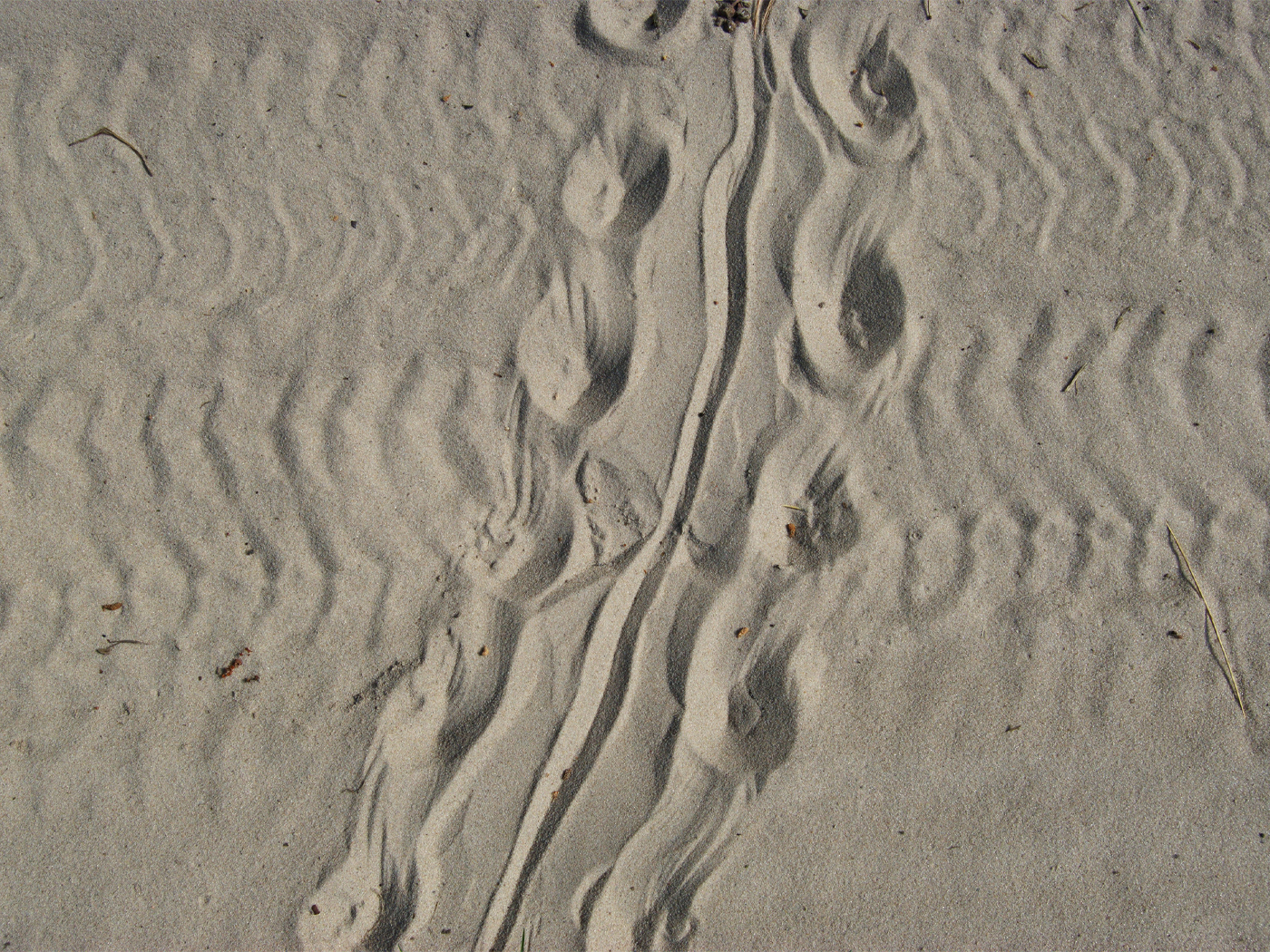
The curious fossil features in question bear the genus name Aspidella and often consist of concentric, circular or oval, disc-like shapes. Most are only a few inches in diameter. Three scientists examined the allegedly ancient fossils, which outcrop in Newfoundland and a few other places, and published their results in Geology.1
The Geology authors proposed a few natural mechanisms, including fluid pipes and collapsed sediments, that might have explained the formation of Aspidella. However, they could not replicate these Aspidella structures in laboratory experiments, a fact that indicates biological origins.
The researchers concluded that Aspidella traces look like animal tracks—specifically, tracks that today's sea anemones might have made.
One clue that sold the researchers on this hypothesis was the pattern of fossil trails showing where several Aspidella discs partly overlapped one another. The underwater animals left these trails as they were sliding sideways through mud in different directions. When the animals pushed slightly upward, they left telltale concentric rings.
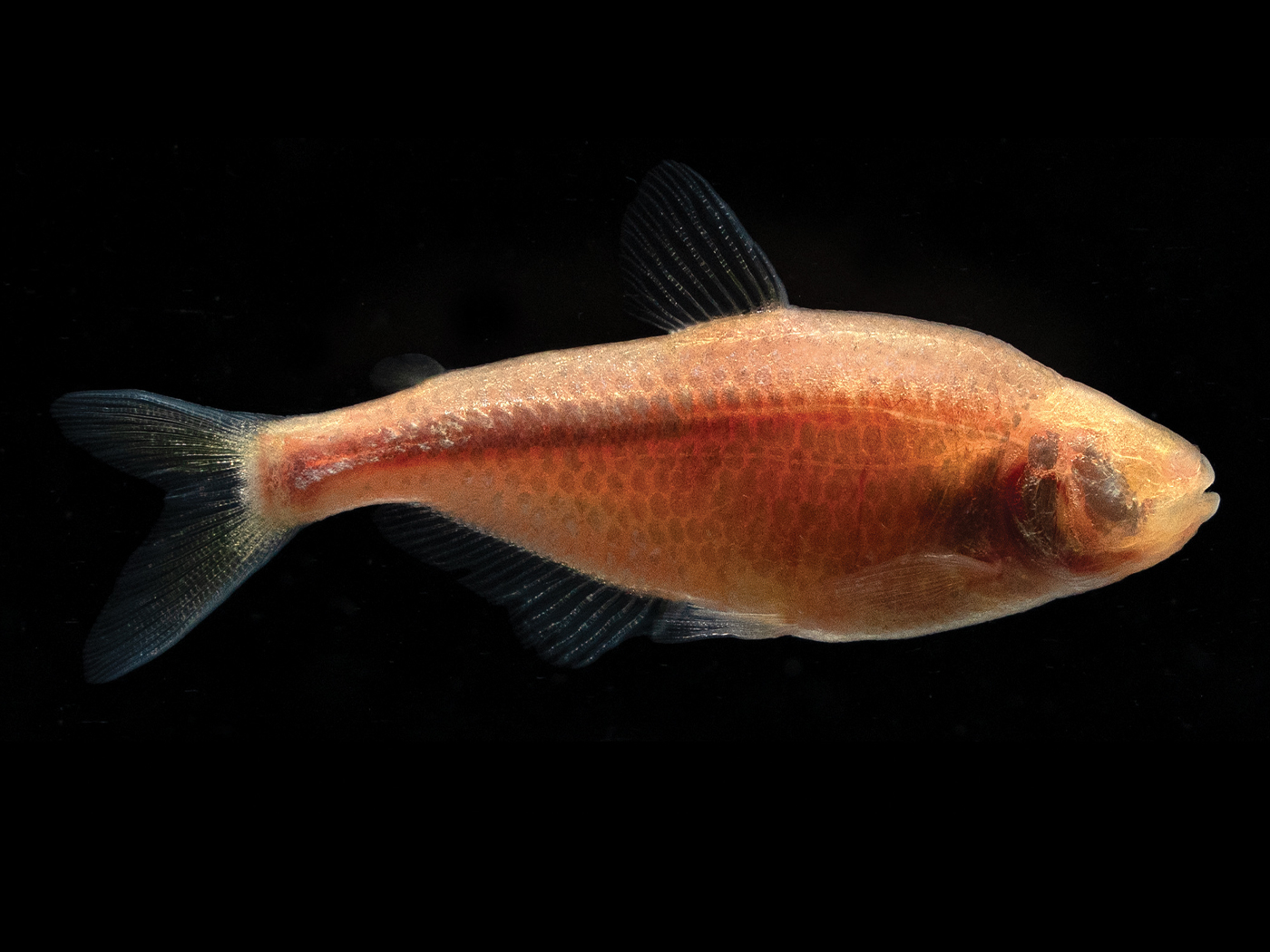
Another clue came by comparing Aspidella tracks to sea anemone anatomy. They match.
Living anemones that inhabit marine mud flats hide most of themselves under a thin layer of sediment but leave a small, upward-pointed mouth exposed to the sea water above, poised to capture and ingest tiny prey. If a storm washes sediment over them, these anemones contract their short, pedestal-like, circular foot then work themselves upward to expose their hungry mouths again. That round foot can leave the same kinds of mud marks that made Ediacaran Aspidella fossils.2
But this implies, in the Geology authors' words, "characteristically animal behavior," including "the ability to respond rapidly to mild environmental stress induced by sedimentation" and movement "by muscular contraction."1
So, right from the start, animals had functioning nerves, muscles, and body shapes integrated with behaviors. In other words, they have always had everything they need to live, just as Genesis asserts.
The clues these scientists uncovered show that creatures still identifiable as living today very likely made the Ediacaran fossil traces. Which idea requires more faith: imagining that 560 million years of mutation and natural selection generated no changes to these mud-inhabiting anemones or understanding that God fully outfitted anemones right from the start?
What were the first animals like? They were like the ones we see today.
References
- Menon, L. R., D. McIlroy, and M. D. Brasier. 2013. Evidence for Cnidaria-like behavior in ca. 560 Ma Ediacaran Aspidella. Geology. 41(8): 895-898.
- Many Flood geologists generally regard Ediacaran strata, which typically have very few fossils, if any, as sediments deposited during the 1,656 or so years between creation and the Flood.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on September 16, 2013.