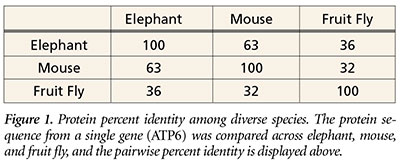
You might expect that the same gene in different creatures would have the same sequence. Surprisingly, this is not so. As we reported last month,1 our preliminary protein/DNA comparison data show profound molecular differences across creatures, and these differences fall along traditional Linnaean classification groupings as shown in Figure 1.
What would you conclude from this result? How did these differences arise? Was this same gene created differently in different creatures? Did these differences arise primarily because of post-creation and post-Flood change? How do we explain these results from a young earth perspective?
One fascinating hypothesis is that these differences arose as a result of different rates of mutation accumulation in different “kinds.” This hypothesis—that the differences stem from different rates of origin—is different from the evolutionary explanation that the differences reflect different times of origin.
Consider the basics of molecular biology for how this might play out practically: The genome (complete set of genetic instructions) in each creature is unique, but genes (subsets of DNA sequence that are ultimately translated to protein) involved in common cellular processes are shared across diverse creatures. If we assume, for example, that God created the same ATP6 (one particular gene involved in energy transformation) gene sequence in elephants, mice, and fruit flies, and if we assume that elephants accumulated mutations slowly; mice, slightly faster; and fruit flies, much faster, then after 6,000 years of mutations, mice would appear (molecularly) different from elephants, and fruit flies would appear even more different from both mammals. Hence, a hierarchy of mutation accumulation rates could produce a hierarchy of molecular differences over time.
Preliminary data on species’ rates of mutation accumulation are consistent with the above hypothesis. A key factor in these rates is the speed at which species reproduce.
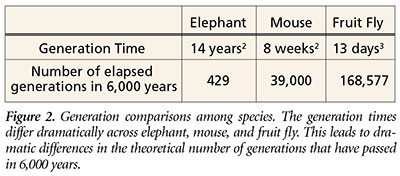 One measure of species’ reproduction rates is generation time—the time from conception to sexual maturity. Comparison of the generation times in elephants, mice, and fruit flies shows a hierarchy of time as shown in Figure 2—elephants reproduce slowly, mice more quickly, and fruit flies the fastest. Conversely, by calculating the theoretical number of generations that have passed in each of these species since creation, it is apparent that fruit flies have had many more opportunities to accumulate mutations than either of the mammals (Figure 2).
One measure of species’ reproduction rates is generation time—the time from conception to sexual maturity. Comparison of the generation times in elephants, mice, and fruit flies shows a hierarchy of time as shown in Figure 2—elephants reproduce slowly, mice more quickly, and fruit flies the fastest. Conversely, by calculating the theoretical number of generations that have passed in each of these species since creation, it is apparent that fruit flies have had many more opportunities to accumulate mutations than either of the mammals (Figure 2).
This very small dataset is consistent with the differential mutation rate hypothesis. However, we have much more data to analyze before we reach any firm conclusions.
References
- Jeanson, N. 2012. Bio-Origins Project Update, Comparing 2,000 Animal Species Molecularly. Acts & Facts. 41 (9): 6.
- Altman, P. and D. Dittmer, eds. 1972. Biology Data Book, Vol. 1, 2nd ed. Bethesda, MD: Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
- Basic Methods of Culturing Drosophila. 2007. Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center at Indiana University. Posted on indiana.edu., accessed July 26, 2012.
* Dr. Jeanson is Research Associate and received his Ph.D. in Cell and Developmental Biology from Harvard University.
Cite this article: Jeanson, N. 2012. Bio-Origins Project Update, Hypothesizing Differential Mutation Rates. Acts & Facts. 41 (10): 6.