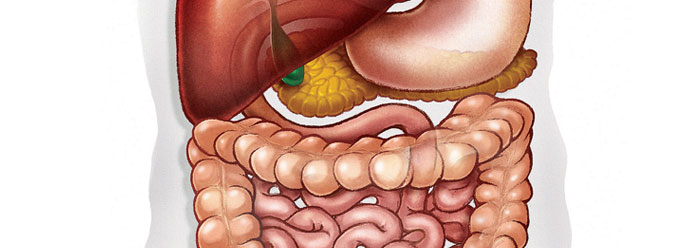
Most people have a passing knowledge of the food they eat, and perhaps how it gets digested. As with all human body systems, however, details of the digestive or gastrointestinal (GI) tract—including the incredibly rich microbial flora found at the last portion of the small intestine and the entire large intestine—are an amazing testimony to creation.
Indeed, on a given day the bacterial population within the human colon usually doubles at least once. This means the common Escherichia coli (E. coli) must replicate (duplicate) its circular chromosome in just 20 short minutes.
The replication of millions of base pairs of DNA is a daunting task in such a small area. The E. coli chromosome must spin at the equivalent of 300 revolutions per second as it makes a second chromosome for upcoming cell division.
A host of unique and diverse bacteria inhabit the large intestine—over 400 bacterial species—and most of them are anaerobic (living in the absence of free oxygen) and are concerned with the production of vitamins K (a fat-soluble vitamin critical in blood clotting) and B.1 It is therefore important to maintain this microbial flora. As long as these bacteria stay put within the GI tract, they do not cause problems; but when they are released into the body cavity or bloodstream (bacteremia), they can cause severe or fatal conditions such as septicemia. This may occur through accidents (or other types of trauma) or disease.
Microorganisms found in the GI tract compete with disease-causing (pathogenic) microorganisms. In biology this is called the principle of competitive exclusion. Normal microbes inhabiting the colon (e.g., the phyla Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Verrucomicrobia) take up the area or ecological niche that disease-causing organisms might otherwise inhabit. For example, a fascinating species of bacteria called Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is designed to survive in the human GI tract in a specific microenvironment (the lumen or cavity) where it breaks down complex carbohydrates with the aid of methanogenic archaea.2
A fairly new field of nutrition involves taking in bacteria called probiotics (pro is Greek for the word “for,” and bios means “life”). Probiotics support digestion and the immune system via the GI tract. Eating foods that naturally contain probiotics has been of increasing interest to the medical field and commercial industry because of their contribution to colonic and overall health. If a person is taking large doses of antibiotics, much of the colonic bacteria would be destroyed. To repopulate the large intestine, a person could eat probiotic foods containing live cultures of bacteria.
As with all areas of biology, secular scientists give an evolutionary explanation to these incredible design features, including the complex interactions of these anaerobic bacteria with the host and with each other. Two evolutionists recently wrote an article regarding “recent evolutionary changes” of these fascinating gut microbes.3 They state—with words like “most likely,” “would have,” “might have,” “may have,” “may explain,” etc.—that there have been changes to the microbiome over human evolution.4 Creationists maintain not only that man has always been man,5 but people have been designed by the Creator to host important intestinal microbes.
References
- Willey, J. M. et al. 2011. Prescott’s Microbiology, 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Ibid, 734.
- Walter, J. and R. Ley. 2011. The Human Gut Microbiome: Ecology and Recent Evolutionary Changes. Annual Review of Microbiology. 65: 411-429.
- Ibid.
- Lubenow, M. 2004. Bones of Contention. Grand Rapids, MI: Baker Books.
* Mr. Sherwin is Research Associate, Senior Lecturer, and Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Cite this article: Sherwin, F. 2012. An Amazing Tract Record. Acts & Facts. 41 (5): 16.