A certain amount of confusion has existed over the use of the term "complex." In the past, creation scientists have used it to refer both to unique arrangements, and to unique, specified arrangements. Evolutionists have capitalized on this ambiguity, insisting that creationists are ignorant of nature’s creative abilities. For example, evolutionary biologist P. Z. Myers reacted to an Acts & Facts article by asserting:
The lesson of Darwin is that unguided natural processes have the ability to generate complex functionality, so it takes more than just showing complexity and function to demonstrate purpose. Creationists don't understand that at all, so they keep whining "it's complex"!2
The reason that "the lesson of Darwin" is rejected by creationists is not because they don't understand it. Rather, it is because they rightly observe that "unguided natural processes" cannot generate both complexity and functionality, referred to as "specified complexity” by Leslie Orgel in his 1973 book The Origins of Life.3 And it is the functionality conferred to a machine by the exact "specification" of its parts that demands a non-natural, purposeful origin.
Specification combined with complexity demonstrates purpose. For instance, the exact configuration of individual sand grains washed up on a beach is extraordinarily unlikely and therefore could be deemed "complex." However, a sand sculpture shaped like a dolphin is both complex (unlikely) and specified (set to the pattern of a dolphin's form). Arguing that waves (i.e., nature alone) can create sand sculptures because both a sculpture and the sand next to it are complex (uniquely arranged) ignores the key distinction: specification to a predetermined pattern.
Using different terms, evolutionary biochemist Jeffrey Wicken explains:
Whereas ordered systems are generated according to simple algorithms and therefore lack complexity, organized systems must be assembled element by element according to an external "wiring diagram" with a high information content.4
Machines with multiple functioning parts are complex in that their parts are uniquely arranged (i.e., lined up in an improbable array). However, any arrangement would be just as unique, just as improbable or complex, as any other. In order to function, the machine needs to have components that are specified to required parameters.
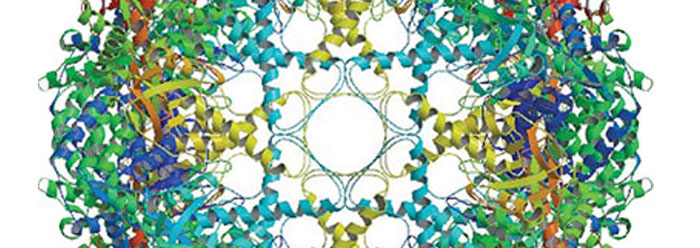
A molecular example is found in chaperonins. In cells, these barrel-shaped protein complexes shelter certain other proteins from watery environments, giving them extra time to fold into their necessary shapes. Chaperonins have a precisely-placed enzymatic active site, detachable caps, flexible gated entryways, a timed sequence of chemical events, and precise expansion and flexion capacities. Each of the parameters--size, shape, strength, hydrophobicity distribution, timing, and sequence--represents a specification. With each additional specification, the likelihood of a chance-based assembly of these parts diminishes…to miracle status.
Nonetheless, hard-core Darwinist Richard Dawkins stated,
The creationist completely misses the point, because he…insists on treating the genesis of statistical improbability [complexity] as a single, one-off event. He doesn't understand the power of accumulation.5
Statistical improbability happens all the time, and by itself is irrelevant to the question of how life originated. Improbability with specification, however, only happens by intention, and it is this combination of qualities for which Darwinian scientists have yet to provide a naturalistic explanation.
Attributing these kinds of creative powers to nature must be a product of the willful exclusion of God, not the product of cogent observation. Since only an all-wise, all-powerful, all-loving Creator could devise nanoscopic, specified-complex, life-sustaining molecular machines like chaperonins (and the biochemical systems that produce them), and since this God is described in the Bible exactly this way, it is most reasonable to credit Him.
References
- Ditzel, L. et al. 1998. Crystal Structure of the Thermosome, the Archaeal Chaperonin and Homolog of CCT. Cell. 93 (1): 125-138.
- Myers, P.Z. Squid and bacteria don't need The Man. Posted on scienceblogs.com/pharyngula on April 1, 2008, 2:58 p.m.
- Orgel, L. E. 1973. The Origins of Life: Molecules and Natural Selection. New York: Wiley.
- Wicken, J. S. 1979. The generation of complexity in evolution: A thermodynamic and information-theoretical discussion. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 77 (3): 349.
- Dawkins, R. 2006. The God Delusion. New York: Houghton Mifflin, 121.
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer.
Cite this article: Thomas, B. 2008. More Than Just "Complex." Acts & Facts. 37 (12): 15.