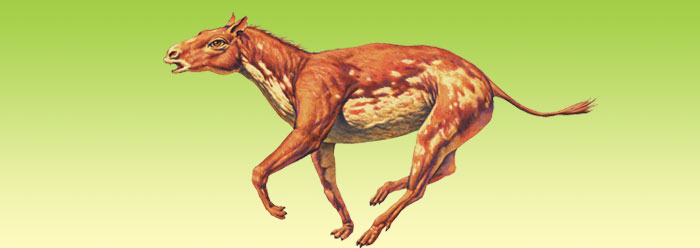
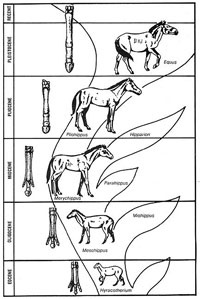
Horse evolution prominently appears in textbooks as a supreme example of the evolution of one body style into another. All students remember the "horse series" sketches, tracing the development of a small browser named Hyracotherium (formerly known as Eohippus) with four toes on the front feet and three on the rear, into the large one-toed horse of today. Intermediate steps included the three-toed Mesohippus, a modified horse with one toe touching the ground; the one-toed Merychippus; Pliohippus, also with only one toe; and finally our modern horse, Equus, who along the way had acquired high-crowned molars and other adaptations.
Of course, modern horses exist in great variety, with many unusual adaptations that allow them to cope with widely varied environments. Numerous species are recognized, almost all of which are known to hybridize. Obviously, there is a great deal of latitude in horse characteristics. Furthermore, various strains can be bred to accentuate one trait, such as the tiny horses about as large as a dog. Horses display a great deal of adaptability.
Early evolutionary theories hypothesized progress in a direct line from one type to another, and fossils were displayed within that framework. In recent decades, this view of directed evolution has been generally disavowed, and no particular form is now considered to have been the goal of "non-directed" mutation and natural selection. Once free to examine the data without this "directed" overprint, evolutionary scientists were quick to recognize that changes among horses had been abundant, extensive, and unpredictable.
 There are some things to note, however. During the same time period that some of the descendants of Hyracotherium supposedly developed into full-blown horses and elephants and other mammals, others persisted unchanged. It seems that evolution does not always change things--often it leaves them alone. Selection pressures that acted so strongly to produce major modifications in some life forms left others in stasis. Their fossils are found in the same strata intervals, so they must have lived in the same environment. Evolution apparently does not apply across the board. If a theory can accommodate any possibility, it is a weak concept indeed.
There are some things to note, however. During the same time period that some of the descendants of Hyracotherium supposedly developed into full-blown horses and elephants and other mammals, others persisted unchanged. It seems that evolution does not always change things--often it leaves them alone. Selection pressures that acted so strongly to produce major modifications in some life forms left others in stasis. Their fossils are found in the same strata intervals, so they must have lived in the same environment. Evolution apparently does not apply across the board. If a theory can accommodate any possibility, it is a weak concept indeed.
It is now acknowledged that horse evolution as recorded in the fossils follows no recognizable pattern, and that the evolutionary "tree" looks more like a multi-branching "bush." The successive forms indicating straight-line evolution appear only in textbooks; they do not appear in the fossils. Sometimes fossils of different types that supposedly lived at different times appear together in the same strata layer. In Oregon, the three-toed grazer Neohipparion (very much like Merychippus) has been found with Pliohippus. In the Great Basin area, Pliohippus has been found with the three-toed Hipparion throughout the timeframe supposedly represented. Evolutionary scientists freely admit this situation--and to their credit often attempt to correct the misconceptions--but still the horse series appears in the textbooks.
Any three fossils can be placed in a line and an evolutionary story can be told about the transformation of one into the other. And a different story could be told if the fossils were arranged in a different order.
It is interesting to note that Hyracotherium was so named because its specimens looked similar to the hyrax. This little "rock badger" can be seen alive in many zoos, complete with an interpretive sign listing its varied evolutionary antecedents. It looks very, very different from a horse, but most of its reputed predecessors could possibly be true variants of the horse. If you took the tiny three-toed ones out of the line-up, then the fossils would fit the creation picture, showing variety within a created kind.
* Dr. Morris is President of the Institute for Creation Research.
Cite this article: Morris, J. 2008. The Mythical Horse Series. Acts & Facts. 37 (9): 13.