Recently, Chinese researchers described their discovery of the “earliest” bird fossil with fused pelvic bones, just like modern birds.1 Also like modern birds, this fossil appears to be made of original bone, not mineralized bone (which would be rock). Could any process preserve actual bones for 120 million years?
This fossil appears to be made of original bone, not mineralized bone. ![]()
The fossil, named Pterygornis dapingfangensis, came from Jehol Biota in northeastern China, and more specifically from a sedimentary rock horizon deemed 120 to 131 million years old. All the other bird fossils with fused hips and arm bones came from later-deposited Cretaceous layers thought to be some 40 million years younger. Thus, the study authors’ main point with this fossil’s description was to reshape the evolutionary origin of birds in a way that would accommodate this 40-million-years out-of-place fossil. But in the process of describing these modern-looking fused bones that challenge tales of flight evolution, these researchers found normal, fresh-looking bird bone.
The PNAS article’s Supporting Information included plenty of familiar bone features. They used a microscope to peer inside this fossil bird’s arm and leg bones. The bone tissue has normal-looking Haversian canals—tiny tube-shaped spaces found in the centers of standard bone structures called osteons. The outer rims have denser bone than the hollowed centers.
These researchers found normal, fresh-looking bird bone. ![]()
The study authors described the insides of the radius bone, found fused with nearby bones to form a rigid wing structure well-suited for flight. They wrote, “The ICL [Inner Circumferential Layer] consists of circumferential avascular lamellar bone tissue of endosteal origin and contains flattened osteocyte lacunae.”2 Lacunae are tiny spaces inside bone’s mineral matrix where bone cells live.
Why, after at least 120 million years, do these finely detailed structures still exist? Why haven’t the lacunae, or especially the canals, been filled in with sediment or mineral precipitates after millions of years of Earth’s water cycle? Incessant erosion, deposition, dissolution, temperature change, and precipitation should have devastated these fossils after so much time. The study authors did not ask or answer any questions like these.
They simply reported what they saw—“bone tissue,” not minerals.
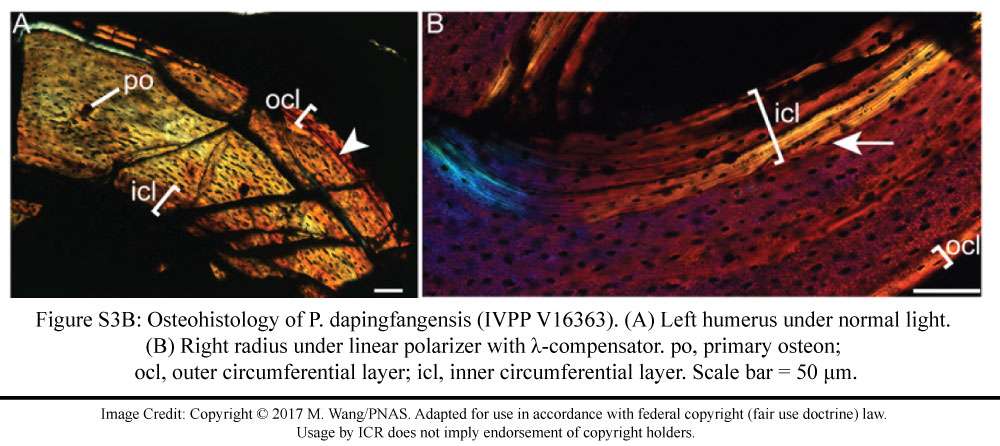
They described the fossil’s OCL (Outer Circumferential Layer)—another familiar structure inside modern bone. They wrote, “This layer exhibits lighter color under polarized light (Fig. S3B), indicating that the collagen fibers are better organized, and the osteocyte lacunae are strongly flattened with their long axes parallel to the external margin of the bone, whereas the osteocyte lacunae in the internal bone tissue are more globular.”2 Although they conducted no chemical test to verify what look like collagen fibers, plenty of other fossils have revealed exactly that—including Chinese fossils like Lufengosaurus.3
They simply reported what they saw—“bone tissue,” not minerals. ![]()
The rare and extinct bird bearing tiny teeth named Pterygornis is not the only fossil from Jehol that has original animal body material. The PNAS study authors referenced a report on preserved eggs, plus seeds, inside Jehol birds.4 They also cited a regurgitated bird pellet containing just-eaten fish bones.5 Plus, the same rocks held a Psittacosaurus so well preserved that its skin, including original skin color patterns, persists to this day.6
If Noah’s Flood buried this bird in the widespread Jehol sediments alongside thousands of other animals—a catastrophic process that does not happen today—then the mystery of how this bone fossil could look so fresh quickly resolves.
References
-
Wang, M., Z. Li, and Z. Zhou. 2017. Insight into the growth pattern and bone fusion of basal birds from an Early Cretaceous enantiornithine bird. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Published online before print. Pnas.or/cgi/doe/10.1073/pnas.1717237114.
- Wang, et al. 2017. Supporting Information.
- Thomas, B. 2017. Stunning Protein Fossils Confirm the Flood. Acts & Facts. 46 (4): 15.
- Zheng, X. et al. 2013. Preservation of ovarian follicles reveals early evolution of avian reproductive behaviour. Nature. 499. doi:10.1038/nature12368(7442): 507-511.
- Wang, M., Z. Zhou, C. Sullivan. 2016. A Fish-Eating Enantiornithine Bird from the Early Cretaceous of China Provides Evidence of Modern Avian Digestive Features. Current Biology. 26 (9): 1170-1176.
- Thomas, B. Scales, Colors, Proteins in Dinosaur Skin. Creation Science Update. Posted on ICR.org September 29, 2016. Reporting results from Vinther, J., et al. 2016. 3D Camouflage in an Ornithischian Dinosaur. Current Biology. 26 (18): 1-7.
Stage Image: Copyright © 2017. Gao, W. Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Beijing. Used in accordance with federal copyright (fair use doctrine) law. Usage by ICR does not imply endorsement of copyright holders.
*Brian Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research and earned his M.S. in biotechnology from Stephen F. Austin State University.
Article posted on October 19, 2017.














