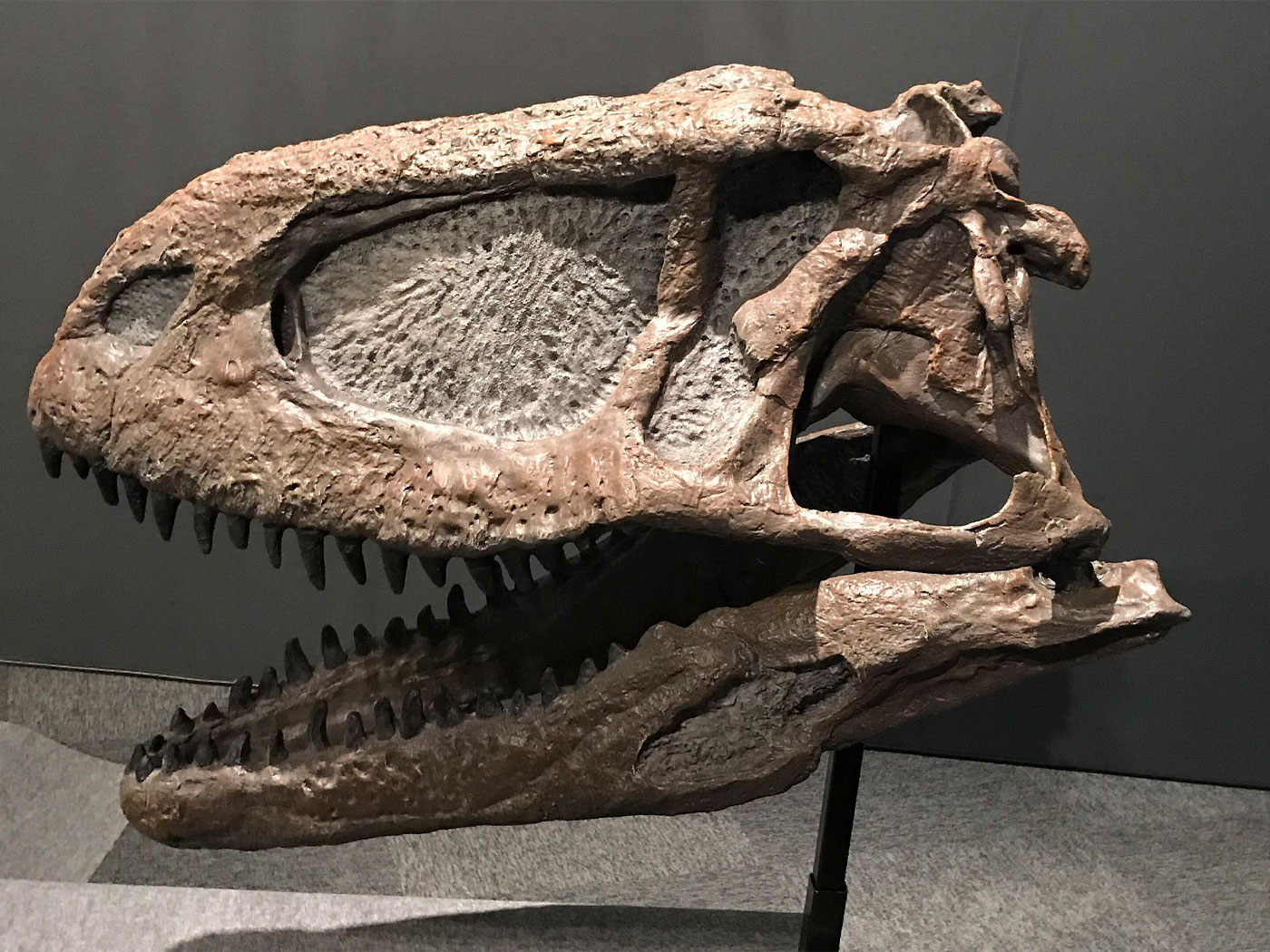
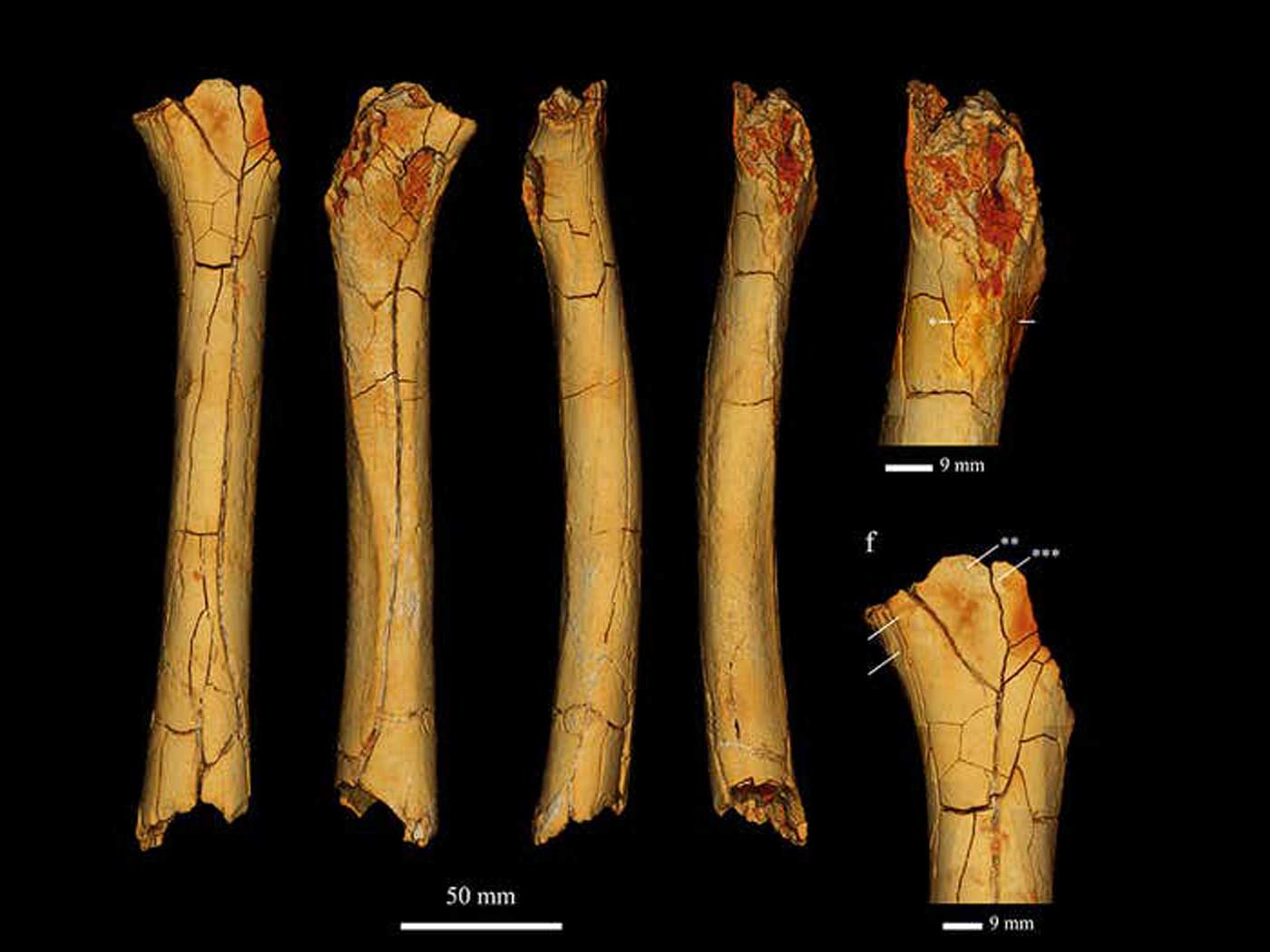
A special set of Australian fish fossils just derailed evolution's long-held story of early fish origins. The remarkable fossils preserved detailed soft tissue body features, including the precise points where muscles attached to the ancient fish's bones. These clues enabled paleontologists to reconstruct the now-extinct fish anatomy. Though expecting something much more primitive-looking, they discovered completely designed, fully-muscled armored fish. Now they have to rewrite the evolutionary bit about how jaws evolved.1
The extinct fish in question are called "placoderms." Australian scientists described how for decades evolution has held to a "shark model" of jaw origins, which had placoderm muscles structured similarly to that of modern sharks. They published their findings in Science.2
Shark skulls hinge side-to-side, and they use side-oriented muscles. But placoderm skulls hinge up-and-down. Of course, they couldn't actually move up and down unless they also had muscles in the right places. The textbook evolutionary tale explains that the first fish to evolve jaws—as opposed to lampreys which have sucker-like mouths without jaws—had not yet evolved the fuller musculature required to move the head and jaws in powerful and effective coordination. These new finds show that placoderms had everything they needed for proper and complete jaw function.
These armored fish "present an anatomy that differs radically from the shark model," according to the study authors.2
Challenging this shark model dogma is a big deal, since placoderms supposedly represent the very first and "most primitive versions of jawed vertebrate anatomy."2 What evolutionist would not be interested in finding out more about the supposed "transition from jawless to jawed vertebrates?"
Lo and behold, placoderms had well-developed neck and trunk musculature that operated their jaws in much the same way as other living animals—but not sharks. The fish's muscles were at some point mineralized, preserving their shapes. These ancient armored fish's muscles held the antagonistic posture required to elevate their heads, open their lower jaws, and snap them together for feeding.
The bottom line? These supposedly primitive fish—purported to represent the advent of jaw evolution—occur fully formed, with no hint of the evolutionary transition that evolutionists had for so long imagined. This discovery forced the study authors to invent a new twist in evolution's old tale. Instead of trunk or stomach muscles evolving eons after the first jaw, they evolved early in these supposedly first-jawed fishes. The muscles then disappeared in later descendants, only to "re-evolve" later still.
The creation explanation needs no such rewrite or side-story. Scripture is clear that the Lord, not nature, designed fish. Scripture also clearly relates how the world suffered a globe-destroying Flood that undoubtedly ended many ocean creatures' lives, as well as air-breathing land creatures not on board Noah's ark. Thus, the Flood is likely responsible for the remarkable mineralization and rapid burial of these Australian placoderms.
Another corollary to the Flood model may explain why these particular fish occur in lower sedimentary layers. It's not because they evolved first. Instead, it's likely because their heavy bony armor slowed them so they were unable to escape fast-moving Flood waters.3
In any case, this finding clearly shows that placoderms, the supposedly earliest jawed fishes, had everything they needed right from the start, just as though they were created.
References
- This episode of evolutionary history already drags baggage, as fossils have so far failed to confirm either of two main competing theories of jaw evolution—the "serial theory" and a more convoluted "composite theory."
- Trinajstic, K. et al. Fossil Musculature of the Most Primitive Jawed Vertebrates. Science. 341 (6142): 160-164.
- For example, world renowned vertebrate fossil authority Clack noted that an Australian fossil cache contained "…a spectacular number of fossil fishes in extensive bedding planes that probably represent mass mortality events. Most of the fishes are placoderms." Clack, J. A. 2012. Gaining Ground, Second Edition: The Origin and Evolution of Tetrapods (Life of the Past). Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press, 78.
Image credit: © Citron / CC-BY-SA-3.0
* Mr. Thomas is Science Writer at the Institute for Creation Research.
Article posted on August 2, 2013.